GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR HYDROCARBON RESERVES
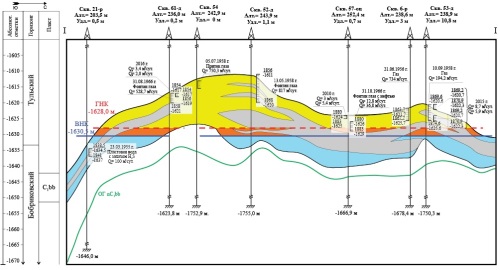
Background. Gas and oil, as well as gas condensate, deposits are challenging objects for research and development. Moreover, as a rule, oil rim reserves are difficult to extract. The advanced production of the gas cap leads to man-made transformations of oil reserves, which significantly complicates their extraction and poses extraordinary tasks for geological and field monitoring and justification of effective geological and technological measures at such facilities. A significant number of deposits, where such advanced development of the gas cap is practiced, are located within the West Siberian, Volga-Ural, and Timan-Pechora oil and gas provinces. The remaining recoverable reserves here exceed the amount of one billion tons. Aim. Analysis of the transformation process of oil rim reserves in the Bobrikovsky horizon deposits of two fields — Goryuchkinskoye and Yuzhno-Generalskoye — in the Saratov Oblast (Russia), along with identification of the main factors affecting the transformation of sub-gas reserves. Materials and methods. The results of geological and field research, development data, and existing geological and filtration models were used as source materials. Geological and commercial analysis was used as the main research method, taking into account the results of reservoir modeling. Results. The considered deposits of the Bobrikovsky formation of the Goryuchkinskoye and Yuzhno-Generalskoye fields have entered an intensive stage of transformation of oil rims. Already at the initial stage, their development was characterized by an active formation of water cones and subsequent movement of oil into the sections previously occupied by gas. The deposits entered the stage of intensive transformation following 5–7 years of the commencement of development. The high reservoir properties and activity of the aquifer contributed to a fairly efficient production of oil reserves. Even without the use of reservoir pressure maintenance methods, significant degassing of oil did not occur. Conclusion. An improved understanding the described processes makes it possible to substantiate effective approaches to regulating the development of deposits, as well as to extracting oil from transformed deposits. This is particularly relevant for objects operated under unfavorable geological conditions and when the transformation process entails irreversible negative changes.
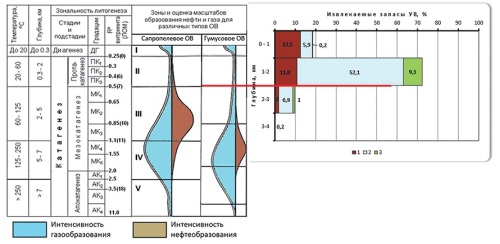
Background. The Illizi oil and gas basin is a key oil and gas region of Algeria. Although large oil and gas fields have been discovered in this region, its potential resources remain to be exhausted. According to the estimates of Zarubezhgeologiya JSC, the forecast oil and gas resources in Algeria as a whole, including the Illizi basin, amount to 837.8 million and 1,470.3 billion tons, respectively3. In order to determine directions for further geological exploration of oil and gas resources, their distribution patterns in the lithosphere should be elucidated. Aim. To determine distribution patterns and formation conditions of oil and gas deposits in Illizi basin by carrying out a statistical analysis of distribution of recoverable hydrocarbon reserves (HC) by deposits, regional oil and gas complexes, and occurrence depths. Materials and methods. The statistical distribution of hydrocarbon reserves was conducted using the data of the Information Handling Services (IHS, 2017) electronic database for the global oil and gas industry. Additional data on the geological structure and hydrocarbon potential of the Illizi basin were taken from literature sources. Results. The Illizi basin demonstrates a significant unevenness in the distribution of recoverable HC reserves. Here, the unique Tin Fuye-Tabancourt deposit and seven large deposits contain 75% of all recoverable HC reserves. The main source of HC deposits are the oil and gas mother rocks of the Silurian Tanezzuft formations, with about 60% of all recoverable HC reserves being concentrated in their immediate vicinity. The greatest concentration of HC reserves is observed in the depth range of 1–2 km (72% of the total recoverable HC reserves in the Illizi basin). The data on the accumulation depth of the main oil and gas areas and the current knowledge of the depth of oil and gas generation indicates significant erosion processes in the post-Paleozoic. Conclusion. The revealed distribution patterns of recoverable HC reserves in the Illizi basin allowed the authors to draw conclusions about the formation conditions of oil and gas fields.
Background. Optimization of the development of residual oil reserves and procedures aimed at in creasing well productivity represents a principal task of subsoil exploitation. Within the Volga–Ural oil and gas province and adjacent oil-bearing zones, acid treatment technologies are among the most common methods for processing the bottomhole reservoir area. However, the existing tools used in the design and planning of these operations neglect several factors that affect their effect iveness, which imposes certain limitations. Aim. To develop a methodology for increasing the effectiveness of computer simulation of acid treatment technologies applied under the conditions of heterogeneous carbonate reservoirs of the Tournaisian stage of the Volga–Ural oil and gas province. Materials and methods. Generalization of the results of operation of more than 100 wells for various purposes using standard approaches for processing and interpreting of geological and field data. Results. Empirical formulas for calculating the duration of reservoir cleaning after treatment, volumes of the highly productive area of wells, and the effectiveness of acid treatments in these areas are presented.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR SOLID MINERAL DEPOSITS
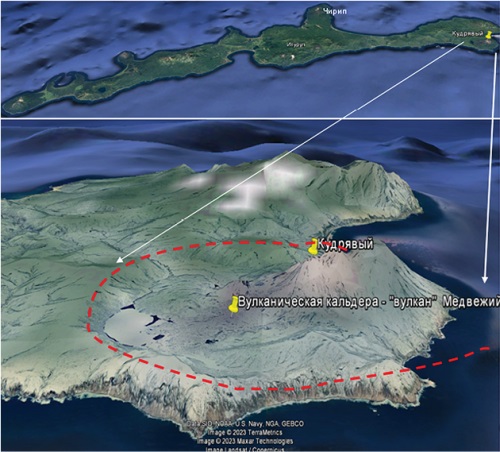
Background. The history of the Archipelago of Kuril Islands and its geological structure are discussed from the perspective of the development of paleovolcanic structures. The magmaticstructure of Iturup Island is analyzed. Prospects for industrial ore mineralization and industrial development are outlined. Aim. To attract the attention of investors to the problem of developing the industrial infrastructure of Iturup Island, which occupies a favorable position in this economic area. Materials and methods. Available materials on the history of exploration, geological structure, and industrial prospects of the area under study are reviewed. Results. Stratiform deposits of lead and zinc are of the same age (Oligocene), regardless of the age of the host carbonate rocks. Conclusion. The geothermal activity of Iturup Island, widely represented in its volcanic structures, is a promising site for the development of the energy industry and extraction of mineral resources.
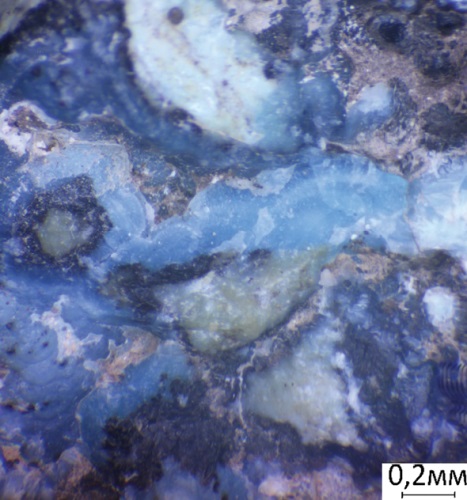
Background. In the quartz veins of the Biryuzakan turquoise deposit, a hydrothermal mineralization of varicolored gibbsite was discovered for the first time. The gibbsite varies from light- to dark blue in color, resembling turquoise. Aim. To conduct a mineralogical study of the gibbsite contained the Biryuzakan vein turquoise deposit. Materials and methods. Stone samples from the Biryuzakan turquoise deposit (northern part of the Republic of Tajikistan), where gibbsite had been found, were collected during fieldworks in 2023. The samples were studied using (1) X-ray phase analysis by a DRON-4-07 diffractometer, with a Cu-anode and a Ni-filter, U — 35 kV, I — 20 mA, imaging speed — 1 deg/min, internal standard — quartz (analyst M. Saimudasiri, Sergo Ordzhonikidze Russian State University for Geological Prospecting) and (2) X-ray microanalysis by a Tescan VEGA 3sbu scanning electron microscope equipped with an Oxford Instruments X-act energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). The analytical conditions were as follows: accelerating voltage — 20 kV, beam current — 20 nA, spectrum acquisition time — 120 s, Certified Standard No. 1362 (Microanalysis Consultants Ltd), MINM25-53 (Astimes Scientific Limited, serial number 01-044) etalons. Results. In the composition of vein formations of the Biryuzakan deposit, we established the presence of gibbsite — aluminum hydroxide — and studied its phase and chemical compositions. The gibbsite veins of Biryuzakan and, possibly, of the Burgundy gold deposit can be attributed to the alunite formation of low-temperature hydrothermal veins. Conclusion. The bright blue gibbsite of Biryuzakan might have been encountered previously bygeologists investigating the deposit for the presence of turquoise. When examining blue samples, turquoise inserts might be misdiagnosed, since blue gibbsite can be visually confused with highgrade turquoise. Our discovery of gibbsite extends the spectrum of mineral associations of the geological object under study and sets the task of inspecting the turquoise mined earlier and products therefrom. The discovered gibbsite is characterized by a complex isomorphism: more than 17% of impurities, including copper, manganese and fluorine (about 5%).
Background. Information on the Dzheltulak large placer system of the Amur gold-bearing province, which has produced 80 tons of gold, is presented. Aim. To determine the geological and structural position of the Dzheltulak placer system, one of the most productive in the Amur province. To characterize placers and sources of their formation. Materials and methods. Published data and stock materials on the geological structure, gold potential, and gold production of the Oktyabrsky ore-placer node were used. Results. The Dzheltulak placer system developed from to an intrusive dome uplift and the gold mineralization of the Oktyabrsky ore placer node. The largest placers are concentrated near the top of the uplift, becoming poorer when moving away from the top. This indicates the centrifugal development of the placer system. The main source of placers is gold mineralization concentrated near the top of the uplift, being represented by gold-bearing areas of skarns and sulfidized limestones (Karlin type of gold mineralization). Conclusion. In order to maintain the level of gold extraction in the Oktyabrsky ore-placer node, identification and exploitation of new gold deposits are required. Among the latter, the most promising area, represented by gold-bearing skarns and deposits of the Karlinsky type, are predicted in the area of Mayachnaya Hill.
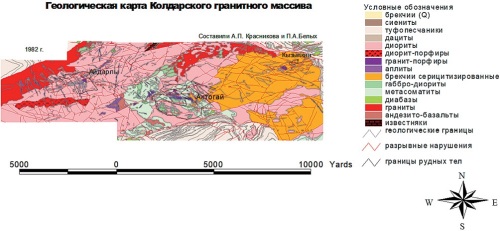
Background. Porphyry copper deposits are attracting increased attention, which determines the relevance of studying their geochemical patterns to ensure a greater efficiency of geological fore casting. Aim. To establish distribution patterns of geochemical elemental associations in porphyry cop per deposits with respect to different levels of erosion by comparing the geochemical features of primary halos at the current level of the erosion section of the Aktogay porphyry copper ore field (Kazakhstan) and the results of geochemical testing of wells of the Sungun porphyry copper de posit (Iran). Materials and methods. A comprehensive geological and geochemical study of a large ore field — the Koldar massif — was carried out in the period from 1982 to 1991. Fieldwork was carried out by the specialists of the Department of Geology, Peoples Friendship University (UDN), in the southern marginal part of the Bakanas depression, considered as the northeastern segment of the Balkhash–Ili volcanic plutonic belt (Central Kazakhstan). A lithogeochemical sampling of bedrock of the Koldar granitoid massif, which includes three porphyry copper deposits (Aktogay, Aidarly, and Kyzylkiya), was carried out. The collected materials were subjected to computer processing. The geochemical data obtained on the Aktogay ore field were compared with the data of deep testing of the Sungun deposit. Lithogeochemical testing of the Aktogay ore field involved spectral, flame photometric (K, Na, Li, Rb, Cs), and atomic absorption analyses of about 1500 samples for the content of 17 elements (Pb, Cr, Ni, Co, V, Mo, Sn, Zn, Bi, Cu, Ag, Au, Li, Rb, Cs, Na, and K). Results. The above-ore, upper-ore, and under-ore levels of the erosion section of the Koldar porphyry copper deposits are clearly identified by quantitative elemental contents in primary lithochemical halos and the following trends in the ratios, typical of porphyry copper mineralization: Cu x Mo/Pb x Zn, Mo/Co, Cu/Mo, Cu x Mo/Cr, Ni/Co. The former two erosion levels of the Koldar deposit are comparable with similar deep levels of the Sungun deposit. Conclusion. The geochemical anomaly of the Kyzylkiya ore occurrence corresponds to the sub-ore level of ore mineralization.
GEOINFORMATICS
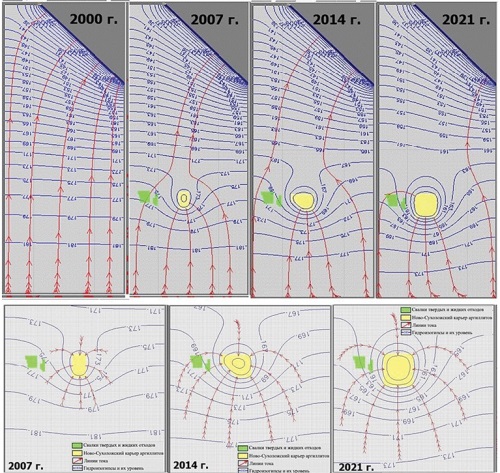
Background. The use of digital twins, created by combining digital models and geoinformation systems, enables a comprehensive description of situations that arise during mining operations. This facilitates informed management decisions and ensures safe and efficient management of mining operations. Aim. Justification of approaches to the creation of digital twins of mining production, which accompany mining operations. Methods. A literature search and review; generalization of the accumulated experience in constructing digital twins of hazardous processes to predict the development of gas dynamic phenomena; control over ore quality and drilling and blasting processes; substantiation of hydro geochemical monitoring and interpretation of its results over prolonged periods using numerical hydrogeomigratory model. Results and discussion. The application of a numerical hydrogeological model as a digital twin confirmed the feasibility of analyzing the results of monitoring and digital modeling for supporting decision making at each stage of quarry development under the action of various factors. The results obtained indicate the prospects of the proposed approach to managing complex hydrogeological and mining systems. Conclusion. The combined use of digital twins and geoinformation monitoring data on hazardous phenomena and processes and their further analysis contributes to increasing the efficiency of mining production.
GEOPHYSICAL METHODS OF PROSPECTING AND EXPLORATION
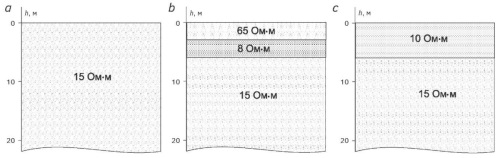
Background. The method of near-field transient electromagnetic sounding (TEM) involves the study of transient fields excited in the earth under the action of changes in the source current. Initially, transient measurements were conducted at times from 100ms and greater; however, in the 1990s, an active study of transient fields in the microsecond range began. Since the microsecond range corresponds to frequencies close to 1 MHz, some parameters of installations, which had been previously neglected, began to attract attention due to their significant contribution to the measured signal. In the 1990s, research was initiated to assess the effect of various installation parameters on measurement results in the microsecond range. At the same time, the effect of the dielectric constant of media in immediate proximity to the generator loop has not been evaluated. Aim. Experimental evaluation of the effect of the dielectric constant of a medium in immediate proximity to the generator loop on the measured transient process. Materials and methods. Field experiments and analysis of the results obtained. Results. The results of measuring transient fields at various parameters of the medium located in immediate proximity to the generator loop are presented. Their analysis is carried out. Conclusion. (1) When working at early (0.1—10 ms) times by the TEM method using an ungrounded current loop as a source, it can be possible to receive signals distorted by processes occurring in the loop itself due to the external parameters of the medium in which the generator loop is located. (2) The shunt resistance should be selected depending on both the size of the generator loop and the effective parameters of the medium in which the generator loop is located.
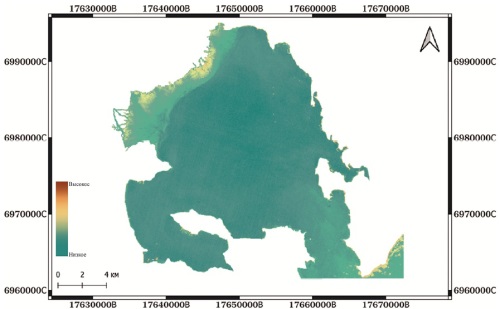
Background. Assessment of the spatial distribution of suspended matter is an essential task in monitoring the ecological state of marine waters. Excessive contents of organic particles, minerals, and fine suspended matter may have a negative impact on ecosystems, reducing water clarity and thereby deteriorating the conditions necessary for photosynthesis. Aim. To assess the sea water turbidity and the spatial distribution of suspended matter in the coastal part of the Avacha Bay using remote sensing methods. Materials and methods. Remote sensing methods are widely used to monitor the state of marine environments through various parameters, such as water turbidity, chlorophyll content, surface water temperature, etc. Modern satellite systems, e.g., Sentinel-2, provide multispectral images for further calculation of spectral indices. In this work, water turbidity was assessed using the normalized difference turbidity index (NDTI). Results. The areas of increased turbidity are formed due to not only anthropogenic impact, but also the geological structure of the environment. The Avacha Bay is a zone under the influence of the Avacha-Koryaksky and other groups of volcanoes. In the spring and summer periods, during active melting of snow and rain precipitation, an intensified flow of the Avacha and Paratunka rivers carrying waterborne volcanic products increases the content of suspended solids in the water. The spatial distribution of NDTI was analyzed, and the maps of water turbidity were compiled. Conclusion. The constructed maps of the spatial distribution of the NDTI index for a number of years showed that the delta of the Avacha and Paratunka rivers, as well as the coastal parts of the Avacha Bay, are associated with increased water turbidity.
GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION TECHNIQUE
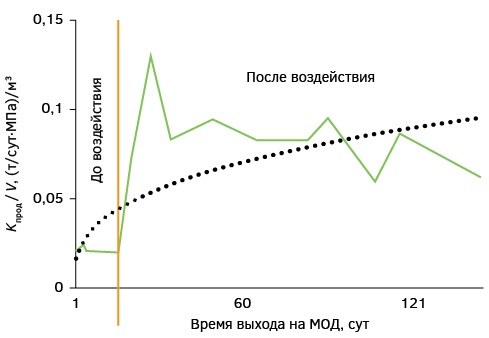
Introduction. Uranium mining by in-situ leaching (ISL) requires the use of special methods for developing wells and maintaining their design productivity (flow rate) both at the construction stage and during operation by carrying out repair and restoration work (R&R). The operation of process wells is accompanied by mechanical, chemical or gas colmatation of filters and near-filter zones (PFZ). In this case, various methods are used to remove the colmatant, which complicates under ground leaching, among which are: mechanical, chemical, physical and combined. This article is devoted to the assessment of the efficiency of using three types of mechanical pulse treatment of uranium SPV process wells at production facilities during their development and repair: pneumatic pulse treatment, using hydrovibrators and pneumatic swabbing. Objective. To provide conditions for increasing the operating period of a production well with productivity at the level of design values. Materials and methods. In this paper, the problem is solved by analyzing the physical nature of the processes occurring, characteristic of the three types of mechanical pulse processing of filters being compared and implemented at enterprises and filter zones, as well as a comparison of the effectiveness of the results of their action, the criterion for which was the volume of working solutions containing a useful product extracted to the surface. Results. The studies have shown that the most effective of the mechanical pulse methods under consideration is the processing of filters and PFZ using hydrovibrators. Conclusion. The use of new technical repair means leads to an increase in the efficiency of ore body development.
MINERALOGY, PETROGRAPHY, LITHOLOGY
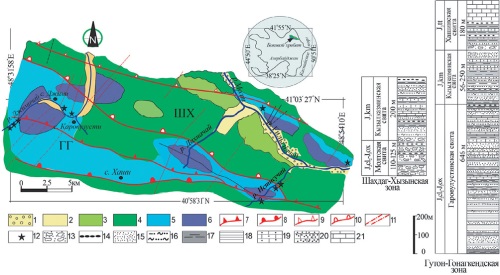
Background. This paper presents the results of complex lithological studies of the Upper Jurassic sediments in the southeastern part of Azerbaijan, the Greater Caucasus area. Aim. Determination of the formation characteristics of Upper Jurassic carbonate-terrigenous rock complexes in the Southeast Caucasus, including paleoclimate, the geochemical regime of the basin, and the petrophysical properties of adjacent erosion zones. Materials and methods. Materials were collected during fieldwork conducted over several years (2015–2023) in the Shahdag-Khyzy and Guton-Gonagkend facies zones of the Side range. The chemical composition of samples was analyzed using a S8-Tiger wavelength-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer. Mineralogical analysis was conducted using X-ray diffraction on a Miniflex 600 diffractometer. Quantitative assessment of mineral content in the samples was based on the intensity of diffraction peaks. For studying the structural and textural features of the rocks, a Carl ZEISS electron microscope was utilized. Results. The data obtained were used to determine the petrochemical properties of the Upper Jurassic sandstone and shale formations in the southeastern Caucasus. Using these parameters, a paleoclimatic and tectonic reconstruction of the formation process of these rocks was also conducted. Conclusion. For the first time, lithochemical modules were calculated and petrochemical characteristics of the Upper Jurassic sedimentary complex of the South-East Caucasus were carried out based on silicate analysis. The chemical composition of the Upper Jurassic rocks is generally uniform, and the distribution of trace elements in these rocks does not show noticeable deviations. Lithochemical parameters of sandstones show a moderate level of maturity, which indicates their formation as a result of mechanical destruction of rocks.
GEOECOLOGY
Background. The data obtained earlier by the authors were used to classify geotoxicological risk factors into natural and anthropogenic, which contributes to ensuring environmental safety and sanitary and epidemiological wellbeing of the population. Aim. Study of geotoxicological risk factors and substantiation of their classification into natural and anthropogenic factors. Materials and methods. The materials collected during the authors’ field, chemical, and biological studies in the middle reaches of the Pechora River and the Opole Voivodeship, Poland, were used. The research methodology was based on observational, experimental, and theoretical analyses followed by generalization of the obtained materials. Results. A methodological approach to determining the similarities and differences of geotoxicological situations in different regions, along with their temporal changes, is proposed. This approach allows identification of the key anthropogenic or natural processes that increase geoecological risks. Conclusion. The proposed approach can be used to determine not only the similarities and differences of geotoxicological situations in different regions and their changes over time, but also to identify key anthropogenic or natural processes that transfer potentially toxic elements to the active phase, increasing the exposure risks of population and the environment.
ISSN 2618-8708 (Online)