HISTORY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Russian scientists, engineers, inventors, and talented entrepreneurs have made a great contribution to the development the Caspian region, one of the main sources of hydrocarbons in the world. In many respects, these specialists have determined the directions of rational development of the oil industry in coastal states and the oil business as a whole. Russian scientists have played an important role in the formation of national scientific schools, which have had a significant impact on the global knowledge in the field. This article memorializes the names of scientists and prominent specialists who have contributed to the development of the oil and gas industry, setting the example of service to the Motherland, Society, and Science. The article is based on the results of a report at the plenary section of the international scientific conference entitled “Formation and development of the oil and gas industry — the contribution of Russian and Azerbaijani scientists and specialists”.
GEOLOGY
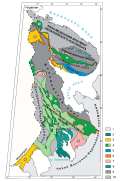
We presented the history of discovery and development of geological hypotheses about the conditions of formation of one of the largest Paloproterozoic structures of the Baltic Shield — the Vetreny Belt. Its uniqueness in relation to the same-age sedimentary-volcanogenic structures of the region is shown, consisting of the formation of volcanics with the spinifex structure, typical only for Archean formations. The unique composition of rocks with good preservation of primary structures and minerals was established for the Vetreny Belt. The experiment proved that volcanic rocks belong to the komatiite series. The problems of stratigraphic and tectonic schemes were considered, some of which are still debatable. The study of the isotopic composition of detrital zircon by LA-ICP-MS from metaterrigenic rocks of the Vetreny Belt hypothesizes calm tectonic conditions of sedimentation, a stable level of erosional shearing, and the age of formation of the structure being Sumian.
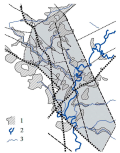
Introduction. Modern geodynamic activity manifests itself in fault zones of aseismic regions as fluctuations in the fluid-gas regime, which determines the importance of gas geochemical indicators.
Aim. Diagnostics of the modern geodynamic activity of fault zones in the Gomel Structural Bridge based on a set of indicators (thickness of Quaternary deposits, relief, hydrographic network, hydrogen and methane anomalies)/
Materials and methods. Studies of the modern activity of fault zones were carried out by indication and geochemical methods (study of subsoil gases and methane content in the troposphere).
Results. The relationship between fault zones and the morpholithogenic basis of landscapes was studied. Based on the anomalous thickness of Quaternary deposits and erosion of Paleogene deposits, glacial troughs controlled by fault zones were discovered (in the northern and southwestern parts of the Gomel Structural Bridge). Gas-geochemical anomalies were recorded in the subsurface air and groundwater. The ground gas geochemical anomalies correspond to increased concentrations of tropospheric methane.
Conclusion. Gas anomalies indicate a different degree of modern activity of fault zones. The greatest geodynamic activity is typical of the northern part of the Gomel Structural Bridge.
Background. New viewpoints on the formation of lead and zinc (Pb and Zn) ore deposits in the People’s Democratic Republic of Algeria are presented.
Aim. To develop a geological and structural model for the formation of Pb and Zn ore deposits in Algeria within the paleovolcanic structure.
Materials and methods. An analysis of the existing materials on the Pb and Zn deposits of the Algerian Republic was conducted. A structural and genetic scheme for the formation of stratiform Pb and Zn deposits in carbonate rocks was proposed using the example of the sulfate-fumarole activity of Mount Erebus volcano.
Results. The stratiform ore deposits of Pb and Zn are of the same age (Oligocene), regardless of the age of the host carbonate rocks.
Conclusion. The stratiform deposits of Pb and Zn are the products of a volcanic sulfate-fumarole activity of hydrotherms under the cover of carbonate deposits formed on the slopes of a paleovolcanic structure of the Jurassic-Oligocene age.
Background. Geochemical signs of magmatic commingling are considered on the example of the Dashkesan Fe–Co deposit using geochemical data and mathematical modeling.
Aim. To develop a petrological-geochemical model of magmatic commingling in the Dashkesan ore deposit.
Materials and methods. The research methodology is based on field data, geochemical data (ICPMS, XRF) analysis of retrospective data and petrographic studies of thin sections.
Results. The influence of the processes of contamination and magmatic commingling is shown using the Dashkesan deposit as an example. This site is associated with the formation of Fe-Co skarn deposits. The rich composition of accessory minerals, variations in textures and structures from hypidiomorphic granular to taxitic, the presence of numerous schlieren and cumulus accumulations of mafic minerals, and numerous xenoliths and enclaves — all are indicative of magmatic commingling processes. The rocks of the first gabbroid phase with increased contents of lithophile and REE elements are characterized by geochemical anomalies; at the same time, lower contents are observed for rocks of further stages of granitoids. The geochemical parameters indicate a relatively enriched magmatic source for the formation of rocks with contamination of the continental crust and subduction-fluid enrichment. These processes led to a deviation in the chemical composition of the Dashkesan rocks from the composition of typical island-arc igneous rocks. The source for the rocks of the gabbro-granite complex was the relatively enriched rocks of the mantle wedge. In addition to the process of melt mixing, the formation of the gabbro-granite complex was accompanied by crustal contamination and subduction enrichment.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR SOLID MINERAL DEPOSITS
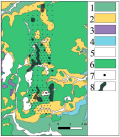
Background. There are prerequisites, signs and manifestations of deposits of strategic types of mineral raw materials Cu, Co, Ni, EPG, Sc, V, REE, hydrocarbons and graphite within the Nakyn, Mirninsky and Syuldyukarsky diamond-bearing fields, which are included, respectively, in the Sredne-Markhinsky, Malo-Botuobinsky and Ygyattinsky districts of the Western Yakut diamond province, there are prerequisites, signs and manifestations of deposits of strategic types of mineral raw materials Cu, Co, Ni, EPG, Sc, V, REE.
Aim. To establish the presence of strategic types of minerals in the diamond-bearing regions of Western Yakutia.
Materials and methods. The study is based on personal documentation of core and spot samples. ALROSA also provided the results of thousands of XRF analyzes that were systematically selected when drilling exploratory wells for kimberlites. Data processing was carried out according to standard statistical analysis methods using the capabilities of the Excel program. Mapping and maintenance of the digital database was carried out in the Quantum GIS (QGIS) environment.
Results. In the Ygyatta district, in the Triassic sills of the Holomolokha intrusion, areas in the rank of potential ore fields of copper-nickel sulfide ores with platinoids of the Norilsk-Talnakh type are localized. In the Late Devonian-carboniferous crust of weathering by kimberlites, there is an ore occurrence of Sc, Co, Ni, V, cerium rare earths. In the Nakyn field, ore occurrences of scandium and manifestations of vanadium and cerium rare earths are localized in the re-deposited weathering crusts of the late Triassic-Early Jurassic age. In the Malo-Botuobinsky district, sites of manifestations of Sc, Si-Ni sulfide mineralization, brown coal, graphite and bitumen as signs of oil deposits, as well as brines with high concentrations of bromine, strontium and lithium were found.
Conclusion. The presented data allows us to establish the presence of various types of minerals in different diamond-bearing regions of Western Yakutia and can become the basis for future prospecting work.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR HYDROCARBON RESERVES
Background. Reservoir flooding is one of the main methods of oil production in low-permeability fields. At the same time, the natural decrease in the effectiveness of the flooding method leads to an increase in the water injection pressure. One of the side effects is the so-called self-induced crack growth in injection wells, which can be accompanied by a crack breakthrough in the production well operation area. A crack breakthrough, in turn, leads to problems associated with unproductive injection.
Aim. To establish the relationship between the development of self-induced hydraulic cracks of technogenic origin with the technological operation parameters of injection wells, the geological properties of formations, the tectonogenetic features of stress distribution across the lower part of the sedimentary cover of the research site (the Priobskoye field).
Materials and methods. Hydraulic fracturing design calculation programs: Planar 3D, FracCADE. Analytical tools: Hall plot.
Results. The relationship between abnormally high reservoir pressures with the phenomenon of technogenic self-induced hydraulic fracturing is determined based on the obtained complications in drilling boreholes, associated with the production of abnormally high reservoir pressures in transit and undeveloped formations. The formation mechanism of self-induced hydraulic fracturing is established. The feasibility of optimizing the current development system in terms of achieving the design oil recovery coefficient of the reservoir is considered.
Conclusion. Optimization of the existing development system at the pilot site of the Priobskoye field using low-permeable reservoirs is proposed. In the case of its successful application, the approach can be used for the entire field, as well as other fields similar in geological structure.
MINERALOGY, PETROGRAPHY, LITHOLOGY
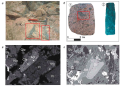
Background. The composition of ores and noble metal minerals (NMM) in the Oktyabrskoe deposit of the Norilsk region varies significantly. An analysis of NMM occurrence forms and their associations may elucidate the conditions of their appearance in ores. Research into the morphology of these minerals is of fundamental importance for solving technological issues of their extraction from sulfide ores.
Aim. To analyze the occurrence forms and associations of NMM to determine their formation conditions.
Materials and methods. In total, 44 polished sections obtained from drill-core holes in the central part of the Oktyabrskoe deposit were examined. The composition and morphology of NNM samples were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy.
Results. Forms of NMM in sulphide ores have been studied and the density of their aggregates has been determined. Different NMM paragenesis depending on the composition of sulphide ores was revealed. The hypothesis of the existence of an inverse relationship between the NMM crystallisation temperature and sulphur fugacity in the ore-forming system was confirmed.
Conclusion. In the central part of the Oktyabrskoe deposit, the composition of NMM and their occurrence forms differ significantly depending of the type of sulfide ores and reflecting the genetic features of their mineralization. Differences in NMM paragenesis indicate a separate, independent evolution of each type of disseminated and massive ores under different conditions. This allows us to update the established model of ore formation in the Oktyabrskoe deposit.
GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION TECHNIQUE
Introduction. The operation of technological wells for underground leaching of metals inevitably leads to a decrease in their design productivity, which is accompanied by an increase in the development time of deposits. This paper shows the impact of the timeliness of repair and restoration work on the efficiency of metal mining, and also substantiates the calculated indicators for determining the duration of repair and restoration work cycles between repairs.
Target. This work is an attempt to analytically develop the main indicator of the duration of the overhaul cycle of the operation of technological wells to determine the frequency of repair and restoration work (RVR) depending on the intensity of the decline in the productivity of borehole in situ leaching (IIL) wells and the coefficient for selecting an effective type of complexes of technical means and technological methods for carrying out RVR.
Materials and methods. This work makes it possible to solve the above problems by approximating the exponential pattern of changes in the productivity of a technological well over time by a linear function.
Results. The specified methodological approach made it possible to obtain the main and derivative indicators: Тм — the duration of the MRC of a technological well, kв — the indicator of restoration of a technological well, kэ — an indicator for choosing an effective type of RWR and to formulate methodological provisions for justifying the frequency of performing RWR of technological wells of SPV uranium to restore them as designed, and the permissible maximum performance.
Conclusion. The resulting dependencies have a simple form and can be used by the linear personnel of the RVR and DPR (production of productive solutions).
Background. Cleaning pipelines and boreholes from contaminants remains an urgent issue. This article discusses a possible solution to removal of destroyed rock, from both the borehole bottom and when transporting cuttings along the borehole length.
Aim. To show the possibility of using pulsed flushing technology to remove cuttings from a borehole. To consider technical means for creating a pulsed flushing flow.
Materials and methods. An analysis of various technical means for creating a pulsed flushing fluid is carried out. A schematic diagram describing the operation of a typical stand for implementing the process is presented. The theoretical aspects of creating a pulsed flushing flow, its vibration frequency, vibration amplitude, and flow rate are considered; formulas for calculating these parameters are given. Technical means for flushing both long pipelines and boreholes are analyzed. A number of patents and technical solutions for removing cuttings from a borehole with a pulsed flow are reviewed.
Results. An assumption is made that calculations of the pulsation frequency of a flushing flow should take into account not only the rotational speed of the rock destruction tool, but also the length of the borehole. This will ensure effective removal of cuttings from the borehole bottom and during their transportation along the borehole length.
Conclusion. The pulsed flushing technology considered in the article can be used for a more efficient cleaning of boreholes from drilling cuttings and other contaminants.
Background. An analysis of the process of hydraulic mining at mines found the absence or irregularity of monitoring of the main parameters of slurry transportation. These parameters include the flow rate and density of the slurry, which determine the hourly output in terms of the rock mass delivered from open pits for processing. This problem impedes regulation of the technological modes of the “open pit–processing plant” hydraulic complex.
Aim. To increase the hourly output of the hydraulic complex operation, the stability of slurry transportation for beneficiation, as well as the extraction of the valuable component.
Materials and methods. Variable pressure measurements were conducted using a hydrostatic densitometer; a Venturi tube flowmeter, including a converging calibration device; a flowmeter with a diverging anti-Venturi device, and a DK-25-40 chamber-type orifice plate. An Induction-51 electromagnetic flowmeter with an accuracy class of 1.5% was used as a calibration device.
Results. The throughput of slurry transportation by the tested flowmeters was found to differ insignificantly in terms of the flow coefficient (about 0.97–0.98). However, the slurry flow rate in the anti-Venturi flowmeter minimizes the wear of the inner walls of the calibration part of the pressure tap. The accuracy of flow measurements depends on the constancy of the Venturi tube cross-section, which is subjected to wear during operation (a runtime of about 650 h and the technological resource in the tests of 110500 m3 ). Substantiation for the application of an anti-Venturi flowmeter is given. Local hydraulic resistances in the diffuser (diverging section) were determined, which mainly depend on such geometric characteristics as the divergence angle α, the divergence degree n, and the diffuser length Іd. The optimal values of geometric parameters were found to be as follows: α=5÷7° at Іd =0.8÷1.5.
Conclusion. According to the results of industrial testing of an anti-Venturi flowmeter at the flow rate of Q=2500 m3/h during several months of mining works, this device can be recommended for application as part of monitoring systems for slurry transportation modes. This device increases the equipment performance and the extraction degree of the valuable component.
GEOPHYSICAL METHODS OF PROSPECTING AND EXPLORATION
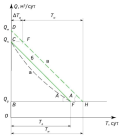
Background. The advancement of geological and geophysical research leverages modern technology to enhance the analysis of instrumental data, particularly focusing on long-wave components of potential fields. This includes studies on temporal gravity variations, which are crucial for understanding the Earth’s kinematics and dynamics, including processes related to earthquakes and volcanism. These variations serve as precursors to such geodynamic events, aiding in the development of predictive models. Aim. This study explores the use of video technology to enhance the digitization and analysis of gravity field variations using the GNU-KV quartz gravimeter.
Materials and methods. The research employed a GNU-KV gravimeter coupled with a specialized video camera. Data captured by this setup were processed using an innovative video recognition algorithm designed for precise and reliable measurement of gravity variations.
Results. The integration of the video camera with the gravimeter facilitated precise digitization of the indicator oscillations. The video recognition algorithm enabled detailed analysis of the gravity variations, improving the accuracy of the results.
Conclusion. Incorporating video technology into gravimetric studies significantly enhances the ability to analyze geological processes, broadening the scope and depth of research in geophysical studies.
GEOECOLOGY
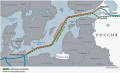
Aim. Assessment of the transboundary environmental damage the Baltic Sea basin during the construction and operation of offshore pipelines. Assessment of the environmental consequences of the sabotage actions associated with the destruction of the Nord Stream offshore gas transportation system, including those associated with the disposal of chemical weapons of the Third Reich and illegal waste disposal in the waters near the island of Bornholm. Integrated assessment of the environmental damage caused to the Baltic Sea basin during the construction and operation of regional and local oil and gas pipelines. Recommendations to the authorities of the Russian Federation on the creation and implementation of legal requirements for environmental damage compensation.
Materials and methods. An analysis of the actual pollution and environmental damage caused to the Baltic Sea basin during construction, operation, and sabotage actions on the offshore pipeline system was carried out using open data. The regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation and their practical implementation were evaluated.
Results. The environmental consequences of the undermining of the Nord Stream offshore pipeline system during sabotage attacks were studied. The impact of the hydrodynamic shock and methane on the Baltic Sea biota was assessed. A consolidated assessment of the environmental damage during the construction and operation of regional and local oil and gas pipelines in the Baltic Sea was carried out.
Conclusion. Recommendations are given to the authorities of the Russian Federation on the creation and implementation of legal requirements related to environmental damage compensation, methods for compensating the damage caused to the property of the Russian Federation and Russian citizens by harmful emissions from neighboring states not in international, but in Russian courts in accordance with Russian legislation.
ANNIVERSARY
MEMORIAL
ISSN 2618-8708 (Online)