GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR HYDROCARBON RESERVES
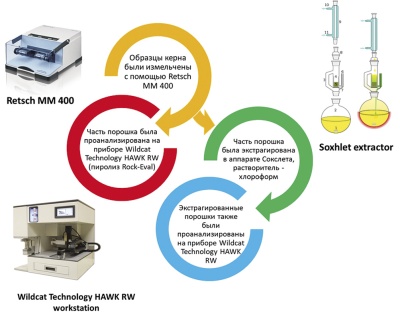
Introduction. Geochemical studies of organic matter in oil source rocks play an important role in assessing oil and gas accumulation in any territory. These studies play a particularly important role in forecasting unconventional resources and oil and gas reserves (so-called shale hydrocarbons). It is recommended to carry out pyrolytic studies by the Rock-Eval method for rocks saturated with organic matter on samples before and after their extraction with chloroform. However, extraction is a laborious and time-consuming process, and the load on laboratory equipment and the time required for analysis is doubled.
Aim. To get a working model for predicting pyrolytic parameters of extracted samples, without carrying out extraction analysis.
Materials and methods. In this paper, machine learning regression algorithms are applied for predicting one of the pyrolysis parameters of extracted samples based on the pyrolytic analysis results of the extracted and non-extracted samples. To develop the prediction model, 5 different machine learning regression algorithms were applied and compared, including multiple linear regression, polynomial regression, support vector regression, decision tree, and random forest.
Results. The prediction result showcases that the relationship between the parameters before and after extraction is complex and non-linear. Some methods have shown their incompatibility with the assigned tasks, others have shown good and satisfactory results. Those algorithms can be applied to predict all geochemical parameters of extracted samples.
Conclusions. The best machine learning algorithm for this task is the Random forest.
Background. The geological structure of the Laptev Sea basin is characterized by a rift nature, thus providing no favorable conditions for the presence of hydrocarbon accumulations. However, the lack of seismic information and the absence of well drilling indicate an incomplete stage of the basin exploration.
Aim. To analyze the results of geological modeling based on structural mapping and to identify promising areas of hydrocarbon exploration. A geological hydrocarbon study of the Laptev Sea basin was carried out in order to recommend areas for licensing, as well as to identify exploration drilling sites and estimate the total initial prospective geological resources according to the conducted numerical basin modeling. To design sedimentation models and predict reservoir properties in the Laptev Sea basin.
Materials and methods. The analysis was based on the data retrieved from production reports for individual large objects in the water area. A model developed by Equinor specialists was used for the basin analysis. The results of hydrocarbon system modeling, the prediction of hydrocarbon saturation obtained from sections of two sample profiles while structural mapping of the basement and top of Oligocene-Miocene sediments were used.
Results. Prospective areas of accumulation of hydrocarbons and their confinement were determined. The probability of hydrocarbons in non-anticlinal traps was estimated. Priority areas of hydrocarbon exploration within the unallocated subsoil area were identified. Recommendations for further geological exploration across the license area were formulated.
Conclusion. Further exploration of the Yuzhno-Laptevomorsky promising area is recommended by means of analyzing the available data, processing of new geophysical data, updating the geological model and designing 3D seismic surveys within the identified promising areas. In addition, 2D seismic surveys at the regional level should be carried out to define the sedimentary boundaries of the Eastern Artic water area.
GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION TECHNIQUE
Background. Technologies applied in geological exploration and mining are undergoing rapid transformations. The scientific progress in this field, which is shifting towards Asia, is characterized by the integration of network and production technologies. The modern society can be conventionally divided into the creative part, i.e. people designing digital technologies, and those operating these technologies. This has become particularly evident with the advancement of the 4th generation of automatics. The period of massive digital transformation started in 2008–2009 with the appearance of the Internet of Things (IoT). This process acquired the term Industry 4.0 or Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Aim. To study current digital transformations in drive control technology applied in exploration and mining equipment.
Materials and methods. Methods and examples of controlling exploration and mining equipment are presented.
Results. The main trends in the development of drive control technology applied in exploration and mining equipment were examined.
Conclusion. Modern digital control systems are capable of re-programming controllers using an active or passive identification of multicomponent multiloop controlled objects in real time. The new Flight Contol Language (FCL) designed for programmable controllers incorporates the methods of fuzzy logic [5,8]. This fuzzy control language uses a new type of data — a linguistic variable, which is a numerical variable with a name, e.g. pressure, rotation speed, temperature, etc., involved in linguistic descriptions.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR SOLID MINERAL DEPOSITS
Background. The Stolbovoe deposit is located in the northern part of the Eastern Sayan, in the Nizhneudinsky district of the Irkutsk region, within the N-47-IX map sheet. The surveying of the territory began in the sixties of the last century. The Stolbovoe deposit was discovered based on direct search signs (radioactivity). At the same time, the search was not aimed at revealing new deposits hidden under the Riphean cover; therefore, most of the territory remained unexplored.
Aim. To map and classify the near-ore hydrothermal-metasomatic alterations manifested on the flanks of the Stolbovoe uranium deposit.
Materials and methods. During the 2018–2020 period, within the framework of prospecting work, the employees of the All-Russian Scientific-Research Institute of Mineral Resources named after N.M. Fedorovsky (VIMS) carried out the mapping of ore alterations using an innovative method of Infrared (IR) spectroscopy. The diagnostics of mineralization was carried out using a portable TerraSpec 4 Hi-Res spectrometer. The instrument was used to measure diffuse reflectance spectra in the Ultraviolet-Visible-Short-Wave Infrared (UV-Vis-SWIR) ranges; the composition of various mineral phases was determined using the TSGVersion 7 database and software.
Results. This study confirmed the efficiency of the method applied for the diagnostics of all varieties of clayey (kaolinite, montmorillonite) and fine micaceous (phengite, sericite, paragonite and their illite varieties) minerals, as well as carbonates (dolomite, ankerite, siderite) and chlorites in the rock in situ or in samples without preliminary sample preparation.
Conclusions. The use of the described method for investigating cores and samples of the Stolbovoe uranium deposit (East Sayan region) made it possible to classify the epigenetic changes in rocks and to map hydrothermal-metasomatic halos, including those near-ore, formed by mineralization that could not be identified by conventional visual and optical methods.
GEOPHYSICAL METHODS OF PROSPECTING AND EXPLORATION
Background. Fractures present in carbonate rocks facilitate fluid flow within void spaces. Each type of voids can have a different effect on rock elastic properties, which, in turn, allow the characteristics of voids to be estimated by assessing the velocity of elastic waves. In this paper, an effect of pores and fractures on the velocity of elastic waves is analyzed by petroelastic modeling. An example of solving an inverse problem is presented, involving the determination of fracture porosity and relative fracture opening using the data on elastic wave velocity and hydrocarbon reservoir density obtained during geophysical well logging.
Aim. To increase the accuracy of experimental data on the velocity of elastic waves that propagate across hydrocarbon carbonate reservoirs by assessing the pore and fracture characteristics of voids.
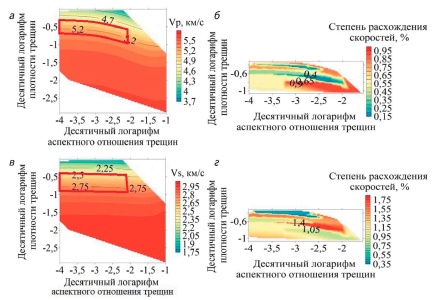
Materials and methods. The effective medium theory was used as an efficient way to evaluate physical, including elastic, properties based on rock composition and microstructure. Using Berryman’s self-consistent method, we created a model of rock elastic properties, or a petroelastic model, the void space in which was represented by isometric pores and fractures. This model was applied to a well in a petroleum province in West Siberia.
Results. The effect of characteristics determining the void space of porous-fractured rocks on the velocity of elastic waves was defined. Velocity surfaces were constructed in accordance with changing parameters of the model, i.e. fracture porosity and fracture aspect ratio. The obtained theoretical and experimental data were compared in order to determine fracture development zones and to evaluate volume concentration and relative fracture opening in these zones.
Conclusion. The effect of pores and fractures on elastic wave velocity in porous-fractured carbonate reservoirs was studied by petroelastic modeling. The zones of excessive fracturing were defined and the parameters of volume concentration and relative fracture opening were determined using the data obtained by geophysical well logging in a petroleum province in West Siberia.
MINERALOGY, PETROGRAPHY, LITHOLOGY
Background. The paper presents new data on the material composition and formation conditions of apatite-magnetite rocks (phoscorite and camaphorites) from the Onkuchakh deposit within the Tomtor massif drawing on the study into the typomorphic features of magnetite.
Aim. To study the morphology, chemical composition, and relations of magnetite with associated minerals in apatite-magnetite rocks from the Onkuchakh deposit (Tomtor massif).
Materials and methods. The study employed core samples measuring 177 m in total length (borehole No. 801, Onkuchakh field, Tomtor massif). In order to determine the composition of recovered minerals, the following instruments were used: JEOL JXA-8230 Electron Probe Microanalyzer (ALROSA, Mirny, Russia); TESCAN MIRA 3 LMU field emission scanning electron microscope equipped with an Oxford Instruments INCA Energy 450+ energy dispersive spectrometer with an XMax-80 detector (ALROSA, Mirny; V. S. Sobolev Institute of Geology and Mineralogy, SB RAS). The measurements were performed according to a standard procedure: accelerating voltage — 20 kV; current — 1 nA; counting time — from 60 s; probe size — 2 μm. Instrument calibration was carried out using a set of characterized artificial compounds and natural minerals; instrument stability was confirmed by measuring Co line intensity.
Results. The authors identified the textural and structural features of magnetite ores, as well as ascertaining their relations with the areas of camaphorites characterized by different material composition and host rocks. The impact of superimposed hydrothermal processes was determined. In addition, a detailed morphological characterization was provided for magnetite found to comprise two generations: primary magmatic magnetite and that transformed under the influence of superimposed processes. Finally, representative data on the chemical composition of magnetite were obtained.
Conclusion. It is concluded that magnetite is formed through a magmatic process involving crystallization differentiation. The occurrence of noble metal is shown to be related to hydrothermal processes superimposed on magnetite ores. The role of apatite-magnetite ores in the formation of the supergene complex — ferrous phosphate lateritic weathering crusts of the Tomtor massif — is confirmed. It is recommended to consider camaphorites from the Tomtor massif as naturally alloyed iron ores potentially extracted along with a number of valuable components.
USEFUL MINERALS, METHODS OF THEIR PROSPECTING AND EXPLORATION
Background. In 2020, the Auditing Chamber of the Russian Federation, based on a representative report by its expert analysts M. Men’ and A. Kaulbars, proposed expanding the search for deposits of a number of metals, including gold. Since the fund of easily discovered gold deposits coming to the surface has been significantly reduced, prospecting of ore regions most promising in terms of gold deposits becomes highly relevant.
Aim. In connection with the above task, it seems expedient to outline territories within the currently known gold provinces, where the prerequisites and signs of gold ores could be detected with minimal expenditures for their subsequent verification by drilling.
Materials and methods. The study involved calculating the shares of the world’s gold reserves attributable to each type of distinguished deposits located in various rocks. The extensive experience of prospecting work carried out in recent decades and culminated in the discovery of the Muruntau deposit in Uzbekistan, a world leader in the development of gold deposits, and Russian largest and giant deposits – Natalka, Sukholozhskoe, Nezhdaninsky, Degdekansky, Maisky, Oktyabrsky, Pavlik, Kupol, as well as the Bakyrchik deposit in Kazakhstan and others, clearly shows that the most promising and largest deposits are selectively localized in favourable rocks and largescale disjunctive dislocations, or faults. To identify favourable rocks, the distribution of the world’s gold reserves in various rocks was analysed, as well as the distribution of reserves in the areas of the largest deposits in ore-bearing faults as the most favourable fault types containing the most powerful and extended gold ore bodies.
Results. A comparison of the shares of reserves has shown that the most promising for prospecting are those rock complexes containing the highest proportions of the world’s gold reserves. The article presents the distribution of shares of the world’s gold reserves for near surface and deep-formed deposits of various types. The main share of the world’s gold reserves in deeply formed deposits is shown to be concentrated in the Phanerozoic strata of sandy-clayey composition and in the interlayers of easily replaceable carbonate and amphibolite shales developed in the Proterozoic quartzite-phyllite rocks. The reserves of near-surface gold-silver and gold-telluride ores are selectively located in the young Mesozoic-Cenozoic volcanic rocks of basalt-andesite composition, accompanied by dikes, subvolcanic stocks and the pipes of explosive breccias with large-scale gold ore bodies confined to them. Thus, the most promising areas for prospecting new deposits are those composed of the mentioned rock complexes and crossed by ore-bearing faults, in the zones of which the main largest ore bodies are concentrated.
Conclusion. The conducted study into the distribution of the world’s gold reserves in the deposits of various types, as well as the selective localization of ores in deposits with the main and large scale ore bodies in the zones of ore-bearing faults (and, accordingly, containing the concentration of the main share of reserves in a particular deposit), provides a basis for discovering new deposits of the precious metal with minimal expenditures, thus contributing to increasing the resource base of the Russian Federation.
MINERAL AND GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION ECONOMICS
Background. The generalization of available information on the volumes of mineral resource waste accumulated in Russia and its use presents a relevant research task. In this regard, an analysis of the current level of use of accumulated mineral resource waste, as well as existing approaches to stimulating the involvement of that waste in economic circulation, is required.
Aim. To substantiate the introduction of adequate and working mechanisms that would stimulate activities for the implementation of projects in the field of mineral resource waste management.
Materials and methods. The present study is based on a systematic analysis of the current Russian regulatory framework in the field of the management of mineral resource waste, relevant scientific publications, as well as the data from the State reports “On the state and protection of the environment of the Russian Federation”.
Results. The level of use of the accumulated mineral resource waste, despite its high resource potential, is two times lower than that in economically developed countries. An analysis of the reasons behind the low level of involvement of various types of mineral resource waste in economic circulation is provided. These reasons include the presence of administrative barriers in obtaining the right to use mineral resource waste and the lack of tax benefits and preferences, as well as the absence of mechanisms for obtaining preferential loans for mineral resource users implementing projects for the processing of such waste. The need to improve the current procedure for obtaining the right to use mineral resource waste objects by introducing a relative declarative is indicated. An analysis of the current mechanisms of tax incentives, guarantee, leasing and financial support for companies implementing projects for processing mineral resource waste is carried out. The insufficiency of these mechanisms and the need to provide additional tax benefits and preferences to such entrepreneurs is pointed out, including the introduction of differentiated MET (mineral extraction tax) rates. In addition, the possibility of using “green” financing mechanisms to stimulate the implementation of projects for the processing of man-made deposits, attracting “long” and “cheap” credit resources in the Russian and international debt financing markets, is analysed.
Conclusion. Stimulating mechanisms for the implementation of projects in the field of mineral resource waste management are proposed, providing for the introduction of a simplified (declarative) procedure for granting small and medium-sized businesses the right to use mineral resource plots represented by man-made objects without bidding and one-time payments, as well as a differentiated approach to the collection of mineral extraction tax in the development of man-made deposits, and the use of “green” financing approaches to attracting concessional credit resources for the implementation of such projects.
CRITICS AND BIBLIOGRAPHY
This article provides a review of the book co-authored by P.A. Ignatov and K.V. Novikov entitled “Field diagnostics of tectonic disturbances and fluid-fracturing formations in kimberlite-containing deposits of the lower Paleozoic” (Mirny: ALROSA, 2019). The book describes a new technique for core sample documentation (along with the conventional technique). The described prospecting wells were drilled within the Nakyn kimberlite field of the Yakutsk diamondiferous province. Of particular interest is the detailed classification and characteristics of tectonic, magmatic, fluid-fracturing and mineralogical features, which contributes to the reliability of kimberlite bodies forecasting. The proposed technique can be used to document core samples from wells of other utility types.
ANNIVERSARY
ISSN 2618-8708 (Online)