GEOLOGY
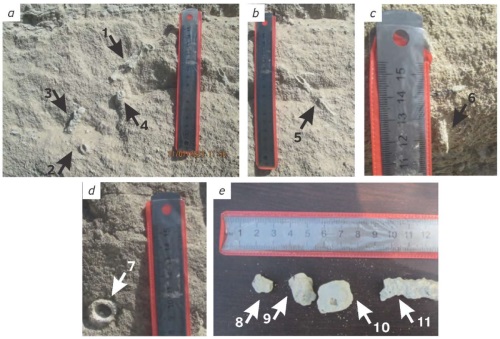
Background. Trace fossils are highly informative objects for geological investigations. However, the information about their distribution in sedimentary settings lacks completeness. The conducted field studies of sandstones of the Hauterivian age in the northern part of Mountainous Adygeya (Western Caucasus) established, to the best of our knowledge, for the first time the presence of ichnofossils in one of their members.
Aim. Characterization and interpretation of an ichnofossil assemblage from Hauterivian sandstones of Mountainous Adygeya.
Materials and methods. Field investigations included in-situ search and documentation of ichnofossils, as well as their sampling. In the course of laboratory investigations, ichnofossils were interpreted; bioturbation and ichnofacies were evaluated. In addition, petrographical and XRD methods were used to analyze the matter that fills the most widespread traces.
Results. The established ichnofossils are distinguished by a low diversity. They can be identified as Ophiomorpha isp., ?Ophiomorpha isp., Skolithos isp., ?Taenidium isp. The latter species, although occurring most commonly, are least clear and hard to identify. Bioturbation is weak, although increasing in particular loci. The ichnofacial interpretation is uncertain due to the coexistence of elements typical of the Scoyenia and Scolithos ichnofacies.
Discussion. The studied ichnofossils indicate the activity of shrimps, insects, and worms both on the surface and inside the sediment. The latter accumulated under the conditions of a subaerial part of the river delta near its stream section. Apparently, in the Hauterivian Stage, the area under study was represented by a land mass.
Conclusion. The results obtained during the conducted ichnological study of Hauterivian sandstones of Mountainous Adygeya are not only interesting per se, but also serve as an important indicator of sedimentation environments.
Background. Selective mining of non-metallic raw materials provides the possibility of shortening the chain of processing and beneficiation operations, while reducing mining waste. Geological and technological mapping facilitates implementation of this approach for many types of raw materials. Implementation of selective mining of carbonate rock deposits requires preliminary forecasting of karst formations in the strata of primary rocks.
Aim. Development of a methodology for geological and technological mapping and to carry out its implementation in the carbonate rock deposits of the Donbass junction zone with the Priazovsky block of the Ukrainian shield.
Materials and methods. The research materials involved the data obtained during geological exploration works on a scale of 1:200,000, documentation of the core of exploration wells, chemical analyses of core and technological samples during the exploitation of carbonate rock deposits.
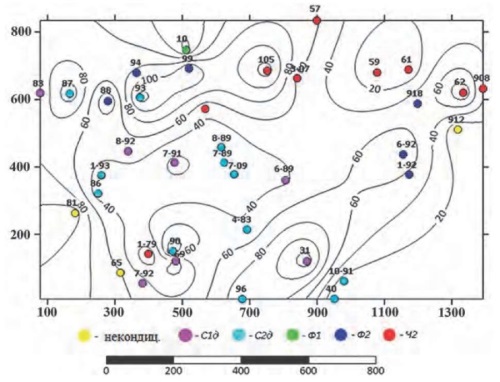
Results. The location of carbonate rock deposits at the junction of two tectonic structures, i.e., Donbass and the Priazovsky block of the Ukrainian shield, which had different signs of the vertical component of tectonic movements during the geological history of the region, led to the block structure of the carbonate strata. The depth of the crystalline basement and the thickness of the carbonate strata installed in the blocks make it possible to determine the spatial position of the blocks with a complete geological section. The large depth of the crystalline basement and the stable position of the block ensured a significant thickness of the carbonate column and the preservation of high-quality primary carbonate rocks. A regression equation between the depth of the crystalline basement and the thickness of the carbonate column is derived, which provides a preliminary forecast of the location of blocks of high-quality carbonate raw materials. This formed the basis for the development of a methodology for identification of blocks of homogeneous carbonate raw materials with subsequent breakdown by grades. The implementation of this methodology in the areas of the Novotroitsk field is described.
Conclusion. The block tectonic structure of the geological formation of the Donbass junction zone with the Priazovsky block of the Ukrainian shield is associated with the preservation of primary rocks and the quality of carbonate raw materials. Geological and technological mapping of carbonate raw materials should be carried out after a detailed analysis of the tectonic structure, which ensures the identification of zones of epigenetic transformations of primary carbonate rocks. It is rational to draw the boundaries of the varietal blocks of carbonate raw materials within the boundaries of individual blocks of the geological structure of the region, rather than within the boundaries of the deposit.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR HYDROCARBON RESERVES
Background. The structure of the Lower Cambrian Moktakon Formation extended across the Yuzhno-Tungusskaya oil and gas region of the Leno-Tungusskaya oil and gas province is studied.
Aim. To develop a sedimentation and storage capacity model of the Moktakon Formation with the purpose of clarifying the oil and gas bearing potential of the region and to elucidate the relations between the selected lithological types and their filtration and storage capacity properties.
Materials and methods. Geological and geophysical data on deep boreholes drilled in the area under study, as well as published and stock materials on the geological structure of the Yuzhno-Tungusskaya oil and gas bearing field were used. Data on 22 boreholes that penetrate the deposits of the Moktakon Formation include: core and cuttings descriptions, test results. Logging diagrams for 15 boreholes that penetrate the Formation to its full thickness were analyzed. Changes in the thickness and composition of the Moktakon Formation sediments were analyzed. A detailed division of the sections into packs, along with correlation of sections and analysis of changes in the filtration and storage capacity properties of rocks, were performed. The methodological basis was formed by works conducted at the All-Russian Research Institute of Oil Geology (VNIGNI).
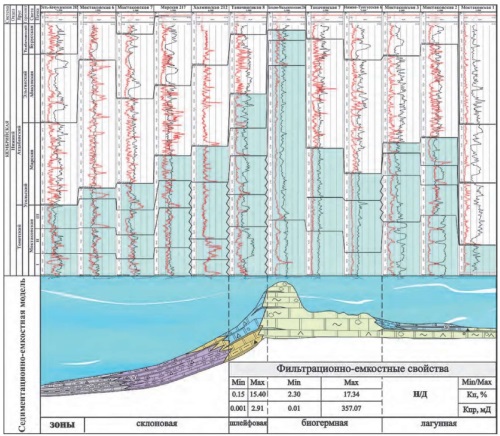
Results. Lithologic types of sediments and section types were determined. Sedimentation conditions were established, including lithologic and facial zones. A sedimentation and storage capacity model of the Moktakon Formation was developed.
Conclusion. The data obtained by analyzing boreholes that penetrate the Moktakon Formation in the western part of the Yuzhno-Tungusskaya oil and gas field were used to compile a sedimentation and storage capacity model of the studied area. This model reflects changes in the composition and thickness of sediments, as well as their structural and textural characteristics. Biohermal, lagoonal, plume, and slope lithologic-facial zones were identified. The suggested sequence reflects the profile of carbonate sedimentation from lagoonal beyond the reef to slope deposits. Biohermal deposits and clastic carbonate sediments of the upper part of the slope are characterized by the best filtration and storage capacity properties.
Background. The junction zone of the Pre-Ural marginal trough and the West Ural outer folding is conventionally considered as a structure possessing a high hydrocarbon potential. However, the complexity of its geological structure, the ambiguity of interpretation of geological and geophysical materials and, as a result, the lack of reliable geological models restrain the development of its resource base.
Aim. To study the formation conditions of sedimentary basins of the junction zone of the Pre-Ural trough and the West Ural outer folding, to characterize the elements of petroleum systems.
Materials and methods. Both unpublished and published geological, geophysical, and geochemical materials on the study area were used. These materials served as the initial data for conducting a basin analysis and an analysis of petroleum systems.
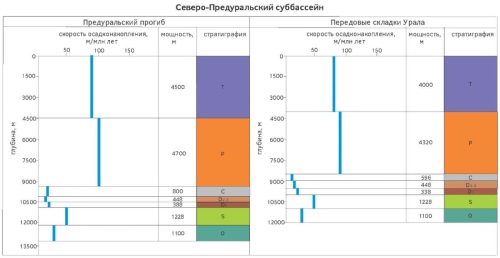
Results. The following three sub-basins were identified: South Pre-Ural sub-basin, Middle Pre-Ural sub-basin, and North Pre-Ural sub-basin. For each subbasin, the average sedimentation rates and sedimentary cover capacities were calculated; elements of petroleum systems were characterized.
Conclusion. The formation conditions of sedimentary basins were studied. The generation and accumulation petroleum systems, which determine the oil and gas potential of the area under consideration, were identified and described.
GEOECOLOGY
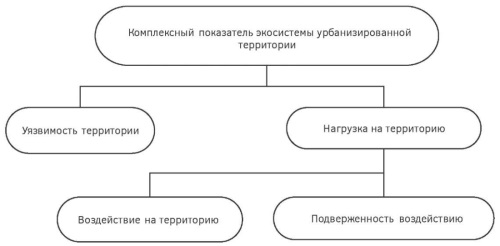
Background. The article substantiates the creation of “eco-maps” of urban areas as a new environmental assessment tool in strategic planning of cities and urban agglomerations. It is assumed that the eco-map of an urban area should serve as a comprehensive ecological map with the possibility of its further development into a dynamic environmental model.
Aim. Development of principles for the creation of eco-maps of urban areas.
Materials and methods. Following an analysis of existing methods for the creation of integrated environmental maps, the basic principles for the development of eco-maps of urban areas are proposed. The importance of their implementation is justified.
Results. The development of eco-maps of urban areas should rely on the following basic principles: (1) various components of the environment should be taken into account, including differences in the mechanisms and rates of changes in their state; (2) the state of urban ecosystems depends not only on the degree of urban load, but also on the vulnerability of the An eco-map is developed based on an integrated ecological indicator of the urban area.
Discussion. The eco-map of a city is a convenient tool for a comprehensive assessment of its ecological state. This tool can be integrated into the existing environmental monitoring system to facilitate reliable forecasting and decision-making processes regarding the development of sustainable urban areas and their adaptation to climate change. This allows for more efficient spatial planning and environmental protection measures aimed at reducing pollution and promoting an ecological culture, which is necessary for the transition to sustainable development.
Conclusion. The existing methods for monitoring the state of urban areas provide either a static picture or display individual ecological parameters, without taking into account the links between them. For comparison, the creation of an eco-map assumes the development of an integrated indicator of the ecological state of urban areas, offering the possibility of combining the developed model with data from comprehensive environmental monitoring. The possibility of creating such eco-maps is justified by the availability of modern technologies for collecting and processing large amounts of data. Thanks to advances in sensor technology, monitoring systems, remote sensing and data processing methods, information about the ecological state of an urban area can be collected in real time. This offers opportunities for obtaining a more comprehensive picture of the state of the environment, based on satellite and ground data.
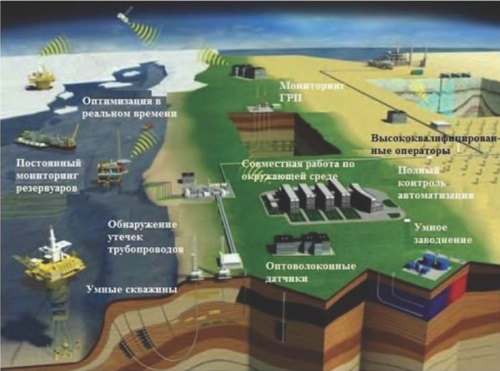
Background. The technologies currently used in the oil and gas industry cannot offer an effective solution to environmental problems. An alternative approach consists in the use of innovative technologies, which combine high productivity with environmental efficiency.
Aim. To review technologies that ensure high productivity in combination with solving environmental problems.
Materials and methods. Artificial intelligence technologies, implementation of digital transformation in solving environmental problems, aerospace methods and technologies, modeling of environmental systems and processes.
Results. The conducted studies revealed the significant potential of the Caspian region in terms of development of alternative energy. Thus, the total wind energy of the Caspian Sea, which theoretically can be used in the Republic of Azerbaijan, is estimated at 157 GW. Out of this potential, up to 35 GW and 122 GW lie in shallow-water (therefore, requiring no substantial expenses) and deep-water areas, respectively.
Conclusion. The use of innovative technologies in the oil and gas industry offers not only environmental but also economic benefits. Reduction of emissions and optimization of the production process decreases pollution risks and the costs associated with elimination of polluting leaks. One of the main challenges of our time is the transition to a new energy paradigm based on technologies that do not contribute to climate change. An energy and ecological revolution is proposed as the most important solution. For environmental monitoring, including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, it is advisable to implement a three-level system of monitoring, diagnosis, and forecasting. This system includes space monitoring; monitoring using unmanned aerial vehicles; monitoring of the underground geological environment based on a geophysical observatory in real time; monitoring gas concentrations using laser absorption spectroscopy and distributed sensor network technology.
Introduction. Shonla is a mountainous province located in the northwestern region of Vietnam, has a complex and diverse terrain with many shapes of hills, valleys and rivers. The assessment of the state of the geo-ecological conditions of the province of Shonla contributes to the development by government agencies of measures aimed at the protection and rational use of the natural environment, which is the basis for the transition to a model of sustainable development and prevention of risks caused by geological processes.
Aim. Studying and assessing the current state of the geoecological conditions in Son La province, Vietnam and the proposal of measures for the transiton to models of sustainable development of the territory.
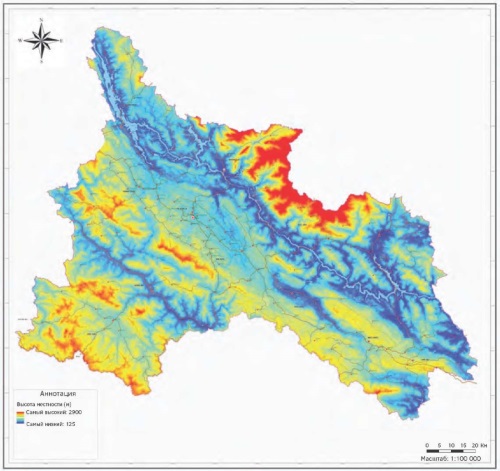
Materials and methods. To obtain information about the geoecological conditions of the territory of the province of Shonla, all previously performed geological, geographical, geodynamic, hydrogeological and other studies were collected, analyzed and summarized. Special attention was paid to the collection of materials for assessing the state and degree of activity of exogenous geological processes. The field research, which was carried out with the participation of one of the authors, included a large complex of geological, hydrogeological, geophysical, hydrological and other methods. Data reflecting the current state of the geoecological conditions of the territory and the degree of impact of the existing functional infrastructure on the environment as a whole were obtained. Remote sensing materials were used to assess the geoecological condition of the territory of Shonla province.
Results. The province of Shonla is a hilly area with steep slopes located along a system of fast-flowing rivers, which creates complex geoecological conditions and indicates the possibility of various geological processes and phenomena that pose a danger during the functional development of the territory. At the same time, Shongla is a territory with favorable conditions for the development of various types of natural ecotourism, which is currently actively developing in Vietnam. The main groups of natural resources located in the territory of Shonla province include land, forest and mineral resources. The study of the geoecological conditions of the province of Shonla (relief and geomorphology, geological structure, hydrogeology, mineral resources) made it possible to identify environmental problems arising from the use of the territory and propose measures for the transition to a model of sustainable development of the region.
Conclusions. In the process of geological development of the territory, the characteristic features of the relief of the province of Shonla were formed. The territory is located in a region with a complex geological structure and the presence of large tectonic fault systems, which increases the risk of geological processes such as earthquakes, flash floods, landslides and others. The assessment of geoecological conditions is a scientific and methodological basis for the development and implementation of measures to prevent natural risks. In order to preserve the unique natural resources, it is necessary to develop and implement a regional model for the transition to sustainable development of the province of Shonla. The results obtained in the course of research can be directly used in construction projects, transport and management structures, as well as in planning the socio-economic development of settlements located in the province of Shonla.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR SOLID MINERAL DEPOSITS
Background. The raw material base of the Republic of Zimbabwe covers numerous endogenic deposits of chromium, nickel, copper, platinum, gold, diamonds, and other minerals. Exogenic deposits are of less occurrence. Most exogenic nickel deposits in the weathering crust and gold ore placers have reached their point of exhaustion. However, there remain prospects for discovering new objects, which determines the relevance of forecasting and prospecting of hidden exogenic deposits in Zimbabwe.
Aim. A geomorphometric analysis of a digital elevation model (DEM) of Zimbabwe with a view to forecasting and prospecting exogenic mineral deposits.
Materials and methods. A digital elevation model (DEM) of the Republic of Zimbabwe was constructed using 120 scenes of the SRTM Void Filled global DEM (SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) version with filled areas of missing data) with a spatial resolution of 3 arcseconds (~90 meters per pixel). The data was obtained through the EarthExplorer service (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov) from the USGS (US Geological Survey). All operations were performed in the open-access SAGA GIS software (http://www.saga-gis.org).
Results. Prospects for discovering exogenic deposits formed in the Neogene-Quaternary period can be assessed by calculating the geomorphometric parameters of the terrain. The conducted analysis of the DEM of Zimbabwe established that its terrain contains the following regional elements of the geological structure: outcrops of the Archean basement, the Great Dyke, Proterozoic formations of the folded framework of the basement, rocks of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic cover. Large terrain segments contain metallogenic taxa, including the Zimbabwean Archean endogenic ore belt. The main watershed divides the area into two geomorphologically different — north-western and south-eastern — parts.
Conclusion. Large terrain segments of the area under study are shown to contain metallogenic taxa, including the Zimbabwean Archean ore belt. An assumption is made that buried placers of gold and platinum, as well as redeposited deposits of cobalt, nickel, and scandium in the lateritic weathering crust should be widespread northwest of the main watershed.
MINERALOGY, PETROGRAPHY, LITHOLOGY
Background. The mineral association of ruby in the Snezhnoye deposit is represented by 7 rock-forming and 19 accessory minerals. Here, all minerals vary in their composition due to isomorphism. The conducted paragenetic analysis of minerals from marble-hosted ruby deposits identified four groups of rocks. Out of them, three groups are divided into series according to the dominant mineral: plagioclase, scapolite, and mica associations. The fourth group comprises monomineralic ruby. The studied minerals exhibit 16 parageneses, including two-, three-, and four-mineral forms. The diversity and uneven manifestation of paragenesis is determined by the variable chemical composition of protolith (bauxite-like sediment), the metamorphogenic transformation of which led to the emergence of Snezhnoye and other deposits.
Aim. To identify paragenetic relations between rock-forming minerals of ruby-bearing deposits.
Materials and methods. The methods of paragenetic analysis, the foundations of which were developed by D.S. Korzhinsky, were used. Three groups of inert elements were selected from the actual mineral and chemical compositions of the Snezhnoye ruby deposits and other ruby-bearing objects of the Muzkol series: (1) Si, (2) Al, and (3) the sum of Ca, Mg, Na, and K. Mineral compositions were calculated in terms of 100% and plotted on triangular diagrams. Then, on the basis of observations in samples and sections on the diagrams, the parageneses were connected by tie-lines for analysis.
Results. The conducted paragenetic analysis of minerals from marble-hosted ruby deposits identified four groups of rocks. Out of them, three groups are divided into series according to the dominant mineral: plagioclase, scapolite, and mica associations. The fourth group comprises monomineralic ruby. The studied minerals exhibit 16 parageneses, including two-, three-, and four-mineral forms. The diversity and uneven manifestation of paragenesis is determined by the variable chemical composition of protolith (bauxite-like sediment), the metamorphogenic transformation of which led to the emergence of Snezhnoye and other deposits.
Conclusion. The use of paragenetic analysis when investigating the metamorphogenic ruby deposit under study produced reliable results, which were further tested at nearby deposits and occurrences. The obtained materials can be used when prospecting new marble-hosted deposits of the Muzkol metamorphic series.
GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION TECHNIQUE
Background. When constructing underground crossings of oil and gas pipelines using directional drilling, the task of enhancing the drilling efficiency becomes urgent. In particular, this concerns the conditions of increased hydraulic resistance and differential pressure. To solve this problem, we propose a new calibrator-ejector design.
Aim. To improve the existing drilling technology by applying a new calibrator-ejector design. The proposed device is equipped with ejection systems for cleaning the borehole, thus increasing the efficiency of directional drilling.
Materials and methods. The problem of increasing the efficiency and environmental friendliness of the process of pilot borehole expansion during the construction of underground crossings of oil and gas pipelines was solved by using reverse circulation and proposing a new design of the calibrator-ejector device.
Results. The possibility of using the same tool at different stages of drilling is shown. This reduces the financial and time expenditures for the construction of crossings. The implementation of the proposed technologies facilitates management of the drilling process and reduces its negative impact on the environment, thus contributing to the development of directional drilling technologies.
CRITICS AND BIBLIOGRAPHY
Sedimentary rocks are essentially the only geological formations that contain oil and gas. Their investigation and description represent a principal research direction in the field of oil and gas geology. The book Oil Lithology by M. A. Tugarova and E. A. Zhukovskaya provides a comprehensive and detailed description of the processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rocks, along with characterization of the major oiland gas-bearing rocks and conventional methods for their study. This book may present interest to specialists in both research and production organizations.
ISSN 2618-8708 (Online)