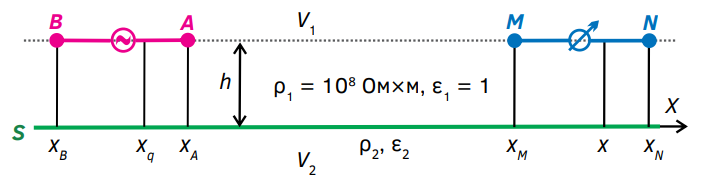GEOLOGIC AND PROSPECTING EDUCATION ISSUES
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR SOLID MINERAL DEPOSITS
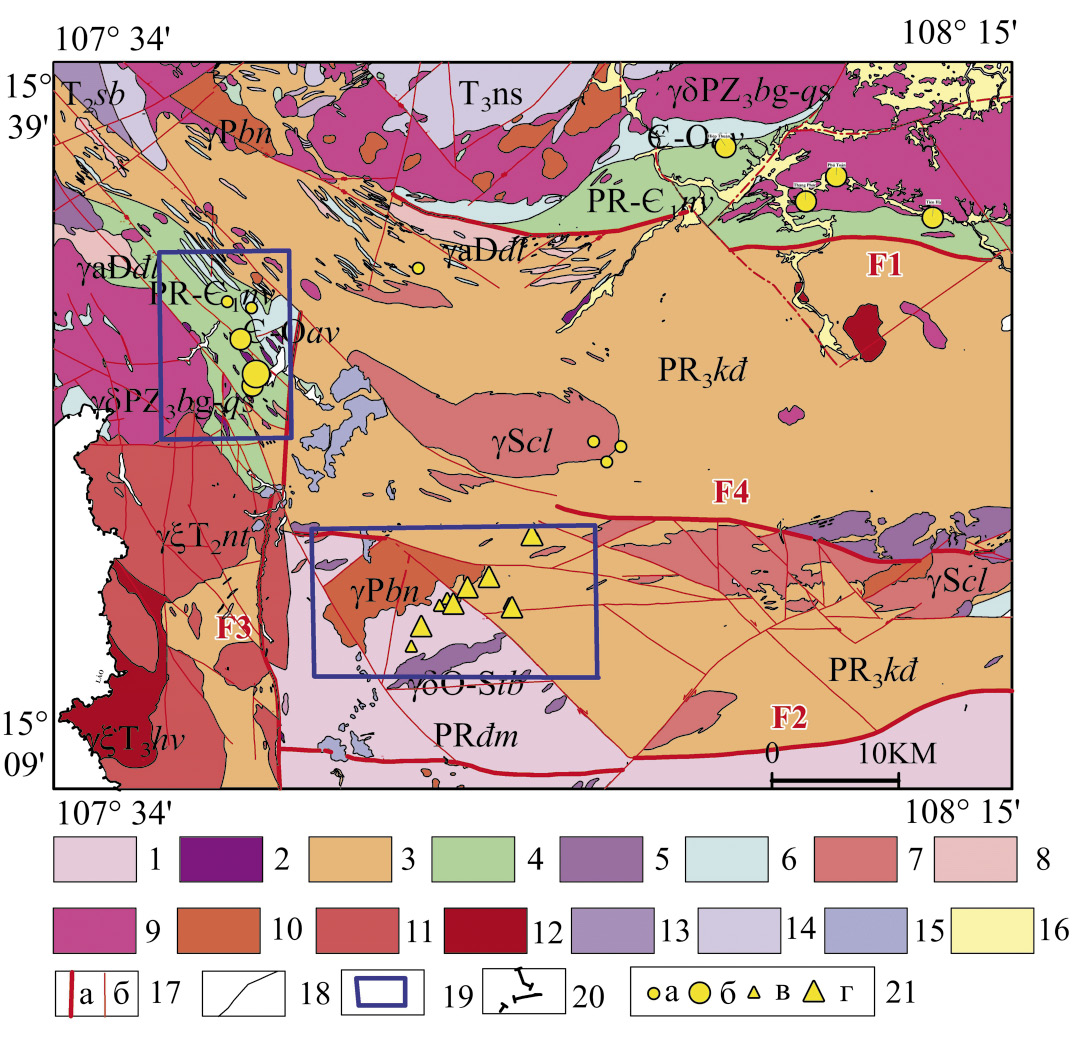
Background. Substantiation for the expediency of typification of gold occurrences in the Phuoc Thanh–Phuoc Son area, Central Vietnam.
Aim. To classify and evaluate the prospects of gold mineralization in the Phuoc Thanh–Phuoc Son area, Central Vietnam.
Materials and methods. The data of geological mapping and exploration of 20 deposits and ore occurrences in the Phuoс Son and Phuoc Thanh ore fields, collected in the 2001–2019 period, were analyzed.
Results. The deposits and ore occurrences of gold-sulfide-quartz and low-sulfide gold-quartz formations of the Late Mesozoic age were established to be common within the Phuoc Thanh– Phuoc Son area. These deposits differ in terms of reserves, ore body morphology, gold-silver ratio, and gold fineness. Conclusion. The results obtained can be used when forecasting the largest gold deposits in Central Vietnam.
GEOPHYSICAL METHODS OF PROSPECTING AND EXPLORATION
Background. Methods for electrical resistance surveys include those of electrical sounding and electrical profiling with various arrays. Measurements were originally carried out at direct current, although low-frequency alternating current was used later. In the case of direct current, the sole sources of the primary electric field in these methods comprise the charges of the A, B current electrodes, with the measured value being the electric field voltage E equal to the potential difference ΔUMN in the MN line with the measuring electrodes M, N. According to the measurement results, the apparent electrical resistivity is determined, which is convenient for interpreting the measurement results ρк. However, in some cases, e.g., when conducting measurements in permafrost areas, it can be difficult to ensure reliable grounding of the electrodes. Therefore, half a century ago, research was initiated to substantiate the possibility of contactless measurements in the method of electrical profiling with the alternating current I in the AB line. Until recently, the technique of non-contact measurements and interpretation of the results obtained has been based on approximate approaches, rather than on a strict solution of the forward problem of electrodynamics.
Aim. Objective substantiation of the non-contact measurement technique based on the solution of a forward electrodynamics problem.
Materials and methods. The data obtained by mathematical simulation were analyzed.
Results. The results of calculations for a model corresponding to the possible conditions for contactless measurements in electrical exploration by the resistance method are presented. A case is considered when a generator line AB of a harmonically varying current I is located in the air, at a height h above a homogeneous conducting half-space with a specific electrical ρ2.
Conclusion. In comparison with the method currently used for non-contact measurements, it seems more effective to determine the apparent electrical resistivity from the reactive component of the electric field voltage E in the measuring line MN that varies in phase with the current I in the generator line AB.
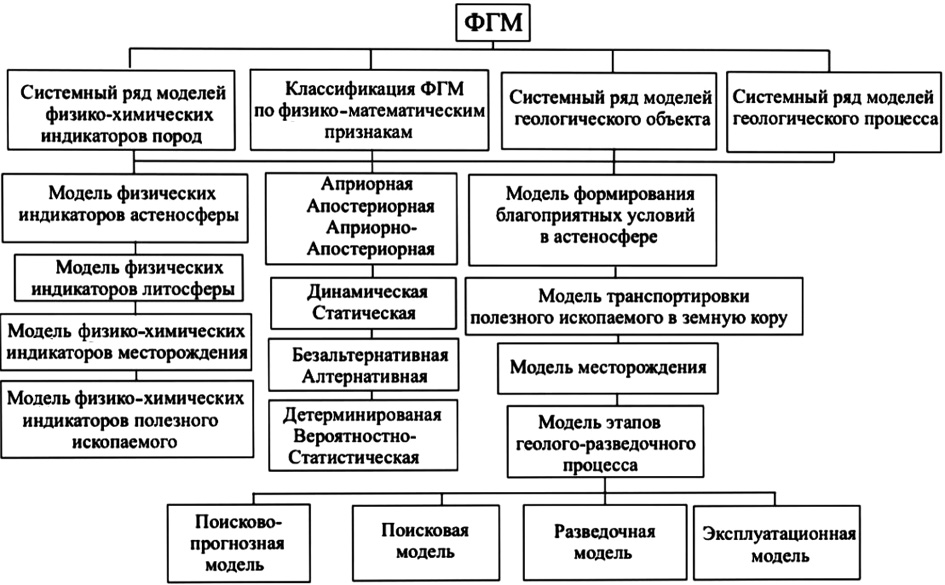
Background. A new classification of physico-geological models (PhGM) is presented, which includes system series of models of physico-chemical indicators, geological objects, and geological processes. Such system series models are characterized by physical-mathematical and geotectonic features.
Aim. Generalization and systematization of existing models and introduction of new model types, which were not previously considered, to propose a new classification of PhGM.
Materials and methods. Scientific publications, including those published by the authors, devoted to the description of various types of models. A systematic review of published data was used as a research method.
Results. The proposed classification of PhGM includes system series of models of physico-chemical indicators, geological objects, and geological processes characterized by physico-mathematical and tectonic features.
Conclusion. A new classification of PhGM is proposed. This classification generalizes the system series of models of physico-chemical indicators and various geological and physical images. System series of models for diamond-bearing kimberlite pipes and earthquakes are presented.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR HYDROCARBON RESERVES
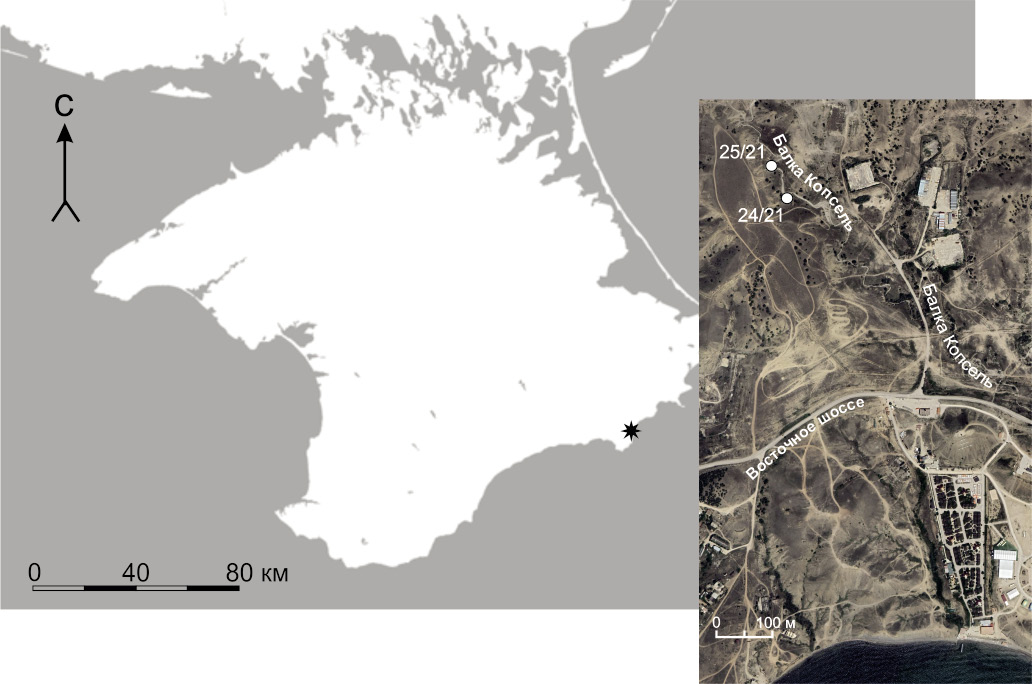
Background. The coal-bearing deposits of the Kopsel formation of the Bathonian-Callovian age of the Middle Jurassic near the city of Sudak (Crimea) are studied. The conducted lithological and mineralogical analysis of rocks, mainly sandstones and siltstones, with shell detritus, plant residues and coal lenses (gagates), made it possible to determine the coastal-marine and lagoon sedimentation conditions. The studied gagates are represented by structural vitrinite and belong to the humus group. Secondary minerals in coal seams and host rocks indicate the stage of early catagenesis. The botanical analysis revealed the coal-forming plants, belonging to a group of conifers of the araucaria family.
Aim. To identify the facies-climatic and landscape conditions for the formation of gagates of the Kopsel formation, along with their composition, structure, and secondary changes. To demonstrate that the material composition of coals is the wood of gymnosperms, mainly conifers, rather than algal thalli.
Materials and methods. The natural outcrops of the coal-bearing deposits of the Middle Jurassic of the Bathonian-Callovian stage of the Kopsel formation in the valley of the Kopsel River near the city of Sudak (Crimea) were studied. The lenses and interlayers of brown coal — gagate — present in these deposits were of particular interest. Gagate samples were studied both macroscopically (forms and occurrence conditions in the section) and microscopically (by coal petrography methods). To this end, double-sided polished sections were examined using a polarizing microscope and a Vega3 Tescan scanning microscope. The microanalysis of chemical elements was performed using an ULTM Max (GIN) microscope attachment. Paleobotanical studies of carbonified plant residues were carried out. The structure, texture and mineral composition of the rocks were studied in thin sections using a microscope. A mineralogical analysis was carried out using a D8 Advace X-ray diffractometer (gross composition in a powder diffractogram and composition of clays in a fraction of <0.001 mm) and a Vega3 Tescan (GIN) scanning microscope.
Results. The comprehensive studies conducted in the new, unique location of coals in the Kopsel Formation of the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian-Callovian stage) in the valley of the Kopsel River determined the paleobotanical composition of coal-forming plants (with the predominance of conifers of the Araucariaceae type), the climatic and paleolandscape conditions for the formation of these coals on the northern outskirts of Tethys. The lithological and mineralogical features of rocks, mainly sandstones and siltstones, with shell detritus, plant residues and lenses of coals (gagates), make it possible to determine the facies conditions of sedimentation as coastal-marine and lagoonal, with fragments of avantdelta and proluvial, landslide deposits. The established secondary changes in the host rocks and the coals indicate the stage of early catagenesis, to which the stratum was subjected at the next stages of geological history.
Conclusion. Peat accumulation and subsequent coal formation most likely occurred in shallow lagoons. The type of peat accumulation is paralytic, paragenetically related to the studied sediments. Post-sedimentation transformations of the rocks correspond to early catagenesis. These transformations were established by the presence of secondary calcite (by rock cracks and in the form of nodule formations), the abundance of authigenic gypsum, and the widespread replacement of pyrite framboids with iron oxide minerals. The interlayers of gagates have also undergone changes. In those places where organic matter is impregnated with carbonate solutions, the coal substance is exposed to heat, thus becoming optically opaque.
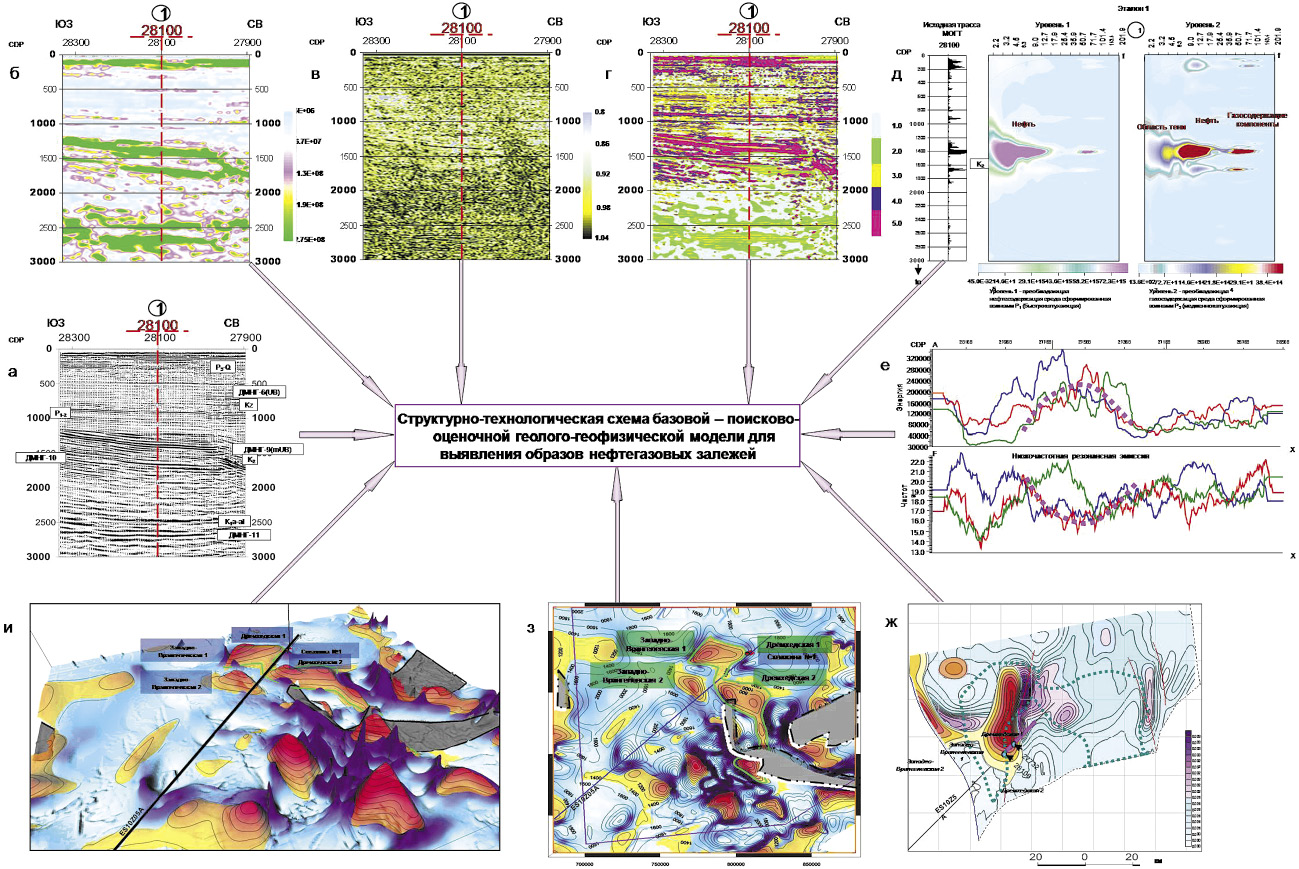
Background. This article analyses the results of geological and geophysical studies conducted in the Okhotsk Sea area with the purpose of developing methods for processing seismic information in combination with other data to solve the problems of forecasting hydrocarbon deposits.
Aim. Solving problems of forecasting hydrocarbon deposits through the development of a structural and technological scheme for prospecting and evaluation of a geological and geophysical model to identify images of oil and gas deposits.
Materials and methods. The research methodology included selection of the location of points for simulating “vertical wells” in order to analyze the geodynamics of the medium; multiplex parametric transformations of wave fields taking into account diagnostic significant attributes and building a multiparametric cluster; selection of oil and gas deposits; formation of images of oil and gas deposits; local forecast of improved reservoir properties and saturation; refinement of the geometry of target surfaces with forecast data in actual points (vertical wells); forecast of the area of target surfaces; spatial mapping of the largest hydrocarbon deposits.
Results. Forecasting of oil and gas prospects in the Okhotsk Sea in areas where there is no deep drilling can be carried out using the following technologies: detailing the structural and tectonic structure of hydrocarbon traps; multi-feature prediction of hydrocarbon deposits; decomposition of the dispersion of the wave field; low-frequency resonance of seismic emission geodynamic noise; selection of oil and gas-containing objects.
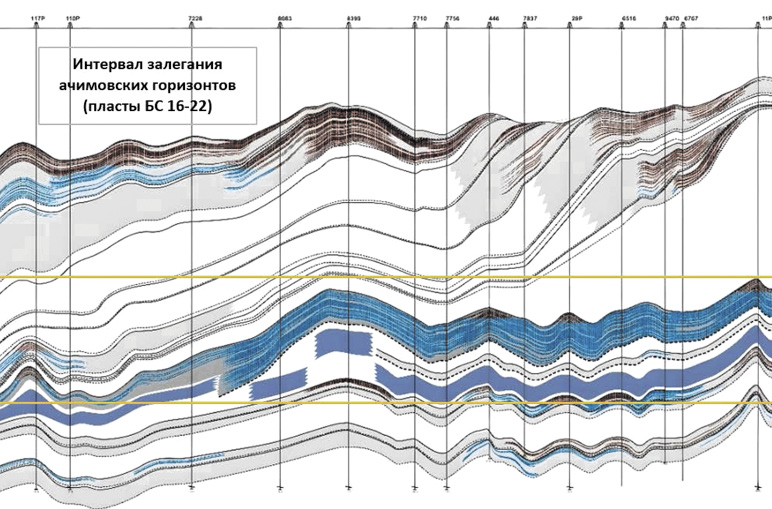
Background. The development of objects that are complex from a geological point of view is characterized by the low efficiency of traditional methods of enhanced oil recovery, the absence or high cost of technological support for production by alternative methods. In this paper, the development features will be considered using the example of an existing object related to the Achimov strata of Western Siberia.
Aim. A retrospective analysis of the dynamics of the development of a production facility, additional study of the possible causes of high water cut.
Materials and methods. To write the work, design documents were used containing data on the geological and physical characteristics and dynamics of production at the production site, as well as graphic applications (geological sections, well logs, extracts from maps). The study of materials, graphic applications and graphing in Excel was carried out.
Results. The possible reasons for the high water cut in the production were studied.
Conclusion. The vector of further development of research activities within the framework of a given topic is determined.
HYDROGEOLOGY AND ENGINEERING GEOLOGY
Background. In recent decades, the concept of weakened zones has become widespread in various fields of Earth science. Thus, this concept is currently used in geology, mining, geomechanics, tectonics, geodynamics, and seismology. As a result, weakened zones can be considered and interpreted both as large fault zones, including dilatancy zones, and zones with sharply or quite noticeably changing physical and mechanical properties. At the same time, the purpose of studying and recording such zones also changes, depending on particular research tasks.
Aim. To consider structures that are widely termed as weakened zones, although having received no clear definition and classification. To provide a definition of this term from the standpoint of hydrogeology and engineering geology.
Materials and methods. The research basis was formed by the author’s long-term experience in the selection of sites for the location of nuclear energy facilities. The main methods included collection, generalization, and processing of information obtained by the author during fieldwork and laboratory research.
Results. The author considers structures that are termed as weakened zones in Earth sciences, concerning a fairly wide range of structures and conditions of mountain ranges and soils. A definition of a weakened zone from the standpoint of hydrogeology and engineering geology is proposed. Various factors indicating the presence of weakened zones and possible negative consequences for engineering structures are considered.
Conclusion. The concept of weakened zones should be taken into consideration when conducting detailed surveys of areas for the location of engineering facilities. It is noted that, when carrying out detailed surveys, the key to quantifying the characteristics of weakened zones in dispersed soils consists in a correct assessment of the spatial variability of soil parameters, largely the density of dry soil and porosity.
ISSN 2618-8708 (Online)