GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION TECHNIQUE
Background. The selection of rational schemes for the technology of hydraulic transportation of rock mass requires optimization of the main parameters of this technology. A large number of factors determining the efficiency of hydraulic transportation hamper the formalization of relationships of the main transportation processes both between themselves and other mining and processing processes.
Aim. To identify specific features of the main processes in hydraulic transportation technology, to establish the factors and parameters that determine their optimal operation, and to propose an optimization tool for both individual links and the entire chain of hydraulic transportation of rock mass.
Materials and methods. The problem of parameter optimization of hydraulic transportation of mineral raw materials is solved based on the integral characteristics of the pressure movement of ore and rock hydraulic mixtures. These characteristics were previously obtained empirically or theoretically by the authors of the present paper and other researchers at various mining companies.
Results. Among the variety of factors determining the efficiency of hydraulic transportation, the size of the transported piece (ore, rock, coal) was found to play the major role. At the same time, the nature of changes in economic expenditures and results of evaluating the effectiveness of hydraulic transportation technology will always relate to a specific field, the accepted technological scheme, and the equipment used.
Conclusion. The problem of parameter optimization of hydraulic transportation processes can be solved using digital twin technology. This technology can be used to address the issues of managing complicated technological processes, as the same time allowing timely adjustments to the modes and parameters of operational processes both on individual production lines and at the enterprise as a whole.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR SOLID MINERAL DEPOSITS
Background. Despite the long history of exploitation and study of Zimbabwe’s geological potential, the ranks of gold ore formations at the level of regions and fields remain unclear. Assessment of the residual primary gold deposits in Zimbabwe appears an important research direction.
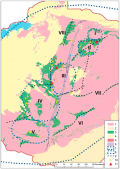
Aim. Identification of ring-shaped and linear ore districts confined to greenstone belts corresponding in configuration within the gold province of the Zimbabwe craton.
Materials and methods. The main method for analyzing gold ore deposits was ore formation analysis. To analyze the residual gold resources in the regions of Zimbabwe, the Zipf-Lotke-Bradford rule was applied according to the ratio of an outstanding rare event in the form of a large deposit, rather rare events in the form of medium-sized deposits, and fairly rare events in the form of small ore objects in a certain ore region.
Results. A hypothesis is proposed for the formation of ring-shaped belts as ore-bearing volcano-tectonic structures of the central type. Within the gold province of the Zimbabwe craton, ore districts of ring-shaped and linear shape, confined to greenstone belts corresponding in configuration, are identified for the first time. It is shown that the localization of deposits in ore regions is due to a combination of the following criteria: ancient faults, arc fragments of greenstone belts, and the development of post-tectonic multiphase granitoid magmatism. A ranking of deposits was carried out in the ore districts of Darwin, Shamva, Midlands, Bulawayo, Gwanda, Busha Mwezi - Fort Victoria, Shashe - Ozi-Umatli, and Sinoia. Five gold mining areas corresponding to volcano-plutonic ring-shape structures and three linear areas were identified. Productivity is predicted to be highest in the Midlands, Bulawayo, and Shamva ring-shape regions. An assessment of the residual gold resources of each of the selected areas is given. The feasibility of detailing important forecast criteria — Late Archean linear and arc faults and post-tectonic granitoids — with the development of additional criteria for further metallogenic zoning and localization of promising areas is established.
Conclusions. The presented data serve as the basis for assessing the prospects of industrially important primary gold deposits in Zimbabwe and carrying out their forecast in the identified gold mining areas.
HYDROGEOLOGY AND ENGINEERING GEOLOGY
Background. Geodynamic processes pose a threat to the infrastructure of any country. Elucidation of these process is crucial for mitigating their impact on the economy, increasing the stability of structures, and ensuring the safety of the population.
Aim. To compile a schematic map of the distribution of the main geological processes in the Republic of Guinea in order to identify the most favorable regions for development while minimizing the consequences of endo- and exogenous geological processes.
Materials and methods. The research involved collection, analysis, and synthesis of geological, geographical, and stock materials. The authors’ own data was also used.
Results. A special-purpose geotechnical map of geological processes in Guinea with a scale of M 1:7,500,000 was created. This map contains information on the spatial distribution of engineering-geological processes in the country. Seven processes that pose a risk to the infrastructure of the Republic of Guinea were identified and classified. The causes, conditions, and rates of process development are outlined.
Conclusion. The developed special-purpose geotechnical map can be used when carrying out macroeconomic planning of the economic development of the country.
GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR HYDROCARBON RESERVES
Background. Tracer well tests were proposed in the last century as an approach for elaboration of detailed reservoir models. Such tests implied injecting weakly adsorbable tracers into an injection well followed by collection and analysis of samples in nearby production wells. The results were assumed to clarify well connectivity and inter-well hydraulic conductivity. However, practical application of these tests showed that the tracer penetrates into the production well much faster than predicted from estimates of the reservoir properties.
Aim. To develop a new technique for interpreting the results of tracer well tests.
Materials and methods. The process of tracer movement along a self-induced hydraulic fracture was simulated taking into account the mass transfer parameter. The developed algorithm for interpreting the results of tracer studies was tested in a deposit located in Western Siberia. The productive interval is located in the Jurassic interval of the Vasyugan Formation. An aqueous solution of thiocarbamide with a concentration of 9% was used as a tracer. Injection was carried out through injection well XX74 for 3 h. The mass of the injected tracer was 1 t. Measurements in six reacting production wells XX72, XX73, XX75, XX76, XX77, and XX78 were conducted for 75 days. During this time period, 516 samples were collected. In the first three days, 36 samples were extracted at equal time intervals; in the following two weeks, 90 samples were extracted also at equal time intervals; during the remaining days, measurements were conducted 2—3 times per week for each well. The results of the conducted studies were interpreted based on the developed methodology for all the wells.
Results. A numerical and analytical solution of the problem of tracer slug movement along the fracture was obtained. Account was taken of the mass transfer between the fluids and the layer, as well as the dissipation of the tracer slug. This solution was used as the basis for a new technique for interpreting the results of tracer well tests, which allows a greater number of fracture parameters to be determined.
Conclusion. The developed technique for determining the parameters of technogenic fractures was applied in practice. The presence of several fractures connecting injection and production wells is shown. It is established that the process of formation of such fractures in the reservoir is still ongoing.
Background. The complex tectonic structure of the Sea of Okhotsk shelf, its high geodynamic activity and the presence of non-anticlinal traps in plays requires special technologies for studying the secondary filtration-volumetric parameters of reservoirs. The prediction of the location and direction of open fractures is complicated by their small size. Such fractures are frequently too small to be detected by such conventional logging or seismic instruments. The detection of fracturing by seismic methods is impossible in principle; however, some high-resolution logging tools are capable of detecting fractures under favorable circumstances. In cases where neither logging nor seismic exploration can detect fractures, geomechanical modeling can be used. Geomechanical modeling makes it possible to predict the effective porosity and permeability in the сrosshole space.
Aim. To assess the geomechanical properties and secondary permeability parameters of the Sakhalin shelf reservoirs.
Materials and methods. The ROXAR reservoir modeling software was used to assess the secondary filtration-volumetric parameters of the Sakhalin shelf reservoirs.
Results. The modern shear stress field was revealed. The permeability of each stratigraphic horizon was calculated. The filtration capacity of local structures was established.
GEOPHYSICAL METHODS OF PROSPECTING AND EXPLORATION
Background. An analysis was conducted out to establish the boundaries of the Kurrachi-Dolomite formation reservoir (Jihar field, Hayan block, Palmyra fold belt). In the process of research, data from geophysical surveys of wells were used and statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out. Currently, due to the difficult situation in Syria, scientific research in this area is extremely limited.
Aim. To conduct a combined processing of geophysical well data (GWD), including by using a correlation matrix, and to assess the applicability the results obtained as an express method for interpreting geophysical data and identifying the boundaries of the Kurrachine-Dolomite formation within the Hayan block and adjacent areas.
Materials and methods. The well data for the empirical study was provided by the Syrian Petroleum Company. Correlation matrices were obtained between the following logging data: CAL, AC, GR, RD, RS, RHOB, and PE. This allowed a good correlation to be determined between their numerical values and the results of core studies, which were carried out to establish lithological characteristics and reservoir properties of the area under study (northwestern part of the Hayan block).
Results. The processed materials made it possible to select the most effective GWD combination for identifying the boundaries and fringe zones of sediments in the Kurrachine-Dolomite formation, considered as a mega reservoir, and to identify priority development objects similar in geological structure and reservoir properties.
Conclusion. The proposed method for processing field geophysical materials (construction of correlation matrices and statistical processing of geological and field data) can be used in selecting an optimal combination of GWD for establishing the reservoir boundaries of the Kurrachine-Dolomite formation, quantifying the reservoir properties, and increasing the efficiency of the Jihar field development (mega reservoir of the Hayan block).
MINERAL AND GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION ECONOMICS
Background. The mineral resource base is a strategic component of Russia’s economic security and a critical tool for strengthening the country’s position in the international arena. At the same time, economic turmoil and geopolitical tensions negatively affect the quality of resource auditing in the oil and gas and other extractive industries of the Russian Federation. This have an effect on the investment attractiveness of exploration projects, which are highly important for the continuous reproduction of the country’s mineral resource base.
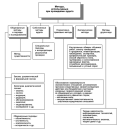
Aim and objectives. In order to consider the potential of mineral resource auditing for augmentation of Russia’s wealth, the following objectives were undertaken: 1) to analyze the structure and state of audit methods in Russian extractive industries; 2) to study the prospects and possibilities of applying international experience in auditing Russian extractive industries; 3) to apply new tools and approaches to optimize auditing activities in the domestic practice.
Materials and methods. Both domestic and foreign research publications were reviewed, along with the reports of the Ministry of Natural Resources and the Environment of the Russian Federation and the Federal Subsoil Resources Management Agency, analytical materials and audit guides by CAAF, INTOSAI, and AFROSAI-E McKinsey. A set of general scientific and special methods Y were used: forecasting methods to assess the state and prospects of financing geological exploration in the Russian Federation; methods of comparative analysis and synthesis, induction and deduction to study the international experience of auditing in the extractive industry.
Results. It is proposed to attract financial resources at various stages of geological exploration through the creation of special-purpose direct investment funds. Attention is also paid to such methods as streaming and acquisition of fixed profit margins from production activities in exchange for an advance payment, which can be applied at later stages of geological exploration.
Conclusion. In order to attract investments for geological exploration of subsoil resources, Russian companies should apply new tools and approaches, as well as international best practices. In combination, this will facilitate the process of attracting funds alternative to budgetary resources, thereby diversifying the methods of financial support, and will increase the investment attractiveness of the Russian geological industry.
HISTORY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Background. The author presents an analysis of the emergence and development of the oil industry in the Kuban and Terek (Grozny) regions in the North Caucasus during 19th—21st centuries, paying particular attention to the Grozny oil industry on the occasion of its 130th anniversary. The process of developing the North Caucasus oil industry is divided into periods depending on the governmental and administration system at different stages of Russian history (Royal Russia, USSR, Russian Federation). As a result, there main stages are defined: 1st stage (Royal Russia for the period of the 19th — early 20th centuries); 2nd stage (USSR); and 3rd stage (Russian Federation). The most important historical events in the course of evolution of the Kuban and Grozny oil industry are given in chronological order. The role of public administration in different historical periods, including revolutionary and war years, economic crisis, and wartime devastation, is shown. The invaluable contribution of Grozny engineers, scientists, and workers of the oil production, oil refining and petrochemical industries to the development of the domestic and world oil industry is demonstrated.
Aim. To analyze the history of formation and development of the North Caucasus oil industry taking into account the role of public administration.
Materials and methods. A large amount of information on Russian history and the history the North Caucasus oil industry was analyzed.
Results. The process of developing the North Caucasus oil industry is divided into periods depending on the governmental and administration system at different stages of Russian history.
Conclusion. To identify the main factors influencing the development of the North Caucasus oil industry, i.e., technological progress and public administration. The latter played a fundamental role in the development of the oil industry in the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation.
CRITICS AND BIBLIOGRAPHY
This book review analyzes historical essays by A.A. Matveychuk about outstanding Russian petroleum geologists. Through the prism of their lives and activities, Matveychuk outlines the first steps in the formation of Russian petroleum geology. Particular attention is paid to the contribution of G.P. Gelmersen, G.V. Abih, and K.I. Bogdanovich, as well as their associates and like-minded people, to the geological study of various Russian regions and to the creation of new organizational structures and scientific schools. It is the activity of the pioneers of petroleum geology that largely determined the shift in the state’s priorities towards oil exploration, which further supported the country’s industrialization in the late 19th—early 20th centuries. The historical events, in which geologists became contemporaries and active participants, were studied. The personalistic approach used by the author in his studies of the initial historical stage of petroleum geology has created a vivid and fairly comprehensive picture of the early history of the industry.
ISSN 2618-8708 (Online)