GEOLOGY AND PROSPECTING FOR HYDROCARBON RESERVES
Background. The article considers paleotectonic and paleogeographic criteria for forecasting hydrocarbon accumulations and determining the sites of priority exploration on the Sakhalin shelf.
Aim. To determine the priority objects of geological exploration on the Sakhalin shelf based on paleotectonic and paleogeographic criteria.
Materials and methods. Generalization and statistical processing of available data, fieldwork materials, reference literature, and scientific publications. Modeling of the tectonic evolution of the Cenozoic sedimentary basin in the studied section of the Sakhalin shelf and its individual sections. The formation and evolution of hydrocarbon systems in the waters of the Sakhalin shelf occurred in the process of geodynamic evolution of the West Okhotsk megabasin covering modern Sakhalin and the adjacent water area. The PetroMod (Schlumberger) and Qgis software packages were used.
Results. The developed paleotectonic and paleogeographic criteria are suitable for both determining the sites of priority exploration and developing appropriate recommendations. Schemes with the allocation of areas that meet the developed criteria were constructed. For all three license areas, the stage of prospecting and evaluation of the oil and gas deposits is required, along with the completion of the exploration and production stage at already discovered fields. Within the license areas, the most promising structures were identified and boreholes were outlined.
Background. The role of dynamocatagenesis in oil and gas formation has been confirmed in a number of publications. However, all of them indicate that dynamocatagenesis manifestations are associated with tectonic disorders selectively. It remains unclear which morphodynamic characteristics of tectonic disorders relate to dynamocatagenesis manifestations, and which values the actual quantitative characteristics of dynamocatagenesis manifestations obtain. Research in this direction is of importance for assessing oil and gas formation in any area, particularly when forecasting unconventional oil and gas resources.
Aim. To determine the reasons for the appearance of anomalies recorded in the deep zonality of the catagenetic transformation of organic matter within the Chezhen Sag of the Bohai oil and gas basin in order to understand conditions for the formation of hydrocarbons.
Materials and methods. Studies were conducted at the borehole level, based on a comprehensive analysis of the latest geological, geophysical, and geochemical information obtained by the Sinopec Shengli Oilfield Company.
Results. At the borehole level, the dynamic type of catagenesis of organic matter was established. A structural-kinematic-age characteristic of faults, to which dynamocatagenesis manifestations are confined, was described. Actual quantitative expressions of thermal impact of faults on the rocks of sedimentary strata were determined.
Conclusion. The conducted research confirmed that anomalies in the deep zonality of organic matter catagenesis are related to dynamocatagenesis manifestations, rather than to the regional immersion.
Background. The production of oil and gas by horizontal wells, despite all its advantages, is subject to exploratory and operational complications. At the final stage of their development, such fields become hard-to-recover reserves. Production of oil and gas is often associated with a high water cut, a significant drop in reservoir pressure, and precipitation of asphaltene deposits.
Aim. To analyze the problem of early indication of flooding of horizontal wells and do research on existing solutions nowadays.
Materials and methods. The dependence of the logarithm of the water-oil ratio on the cumulative oil production was investigated. An analysis of production decline curves was carried out, along with a graphical diagnostics of flooding evolution.
Results. The anticipated cumulative production of a well was determined by continuing the linear dependence to its economic limit. A graph was plotted in semi-logarithmic coordinates for the analysis of production decline curves. According to the dependence of the water-oil ratio versus time, the type of early well flooding was determined in logarithmic coordinates.
Conclusion. One of the most significant problems in the development of horizontal wells consists in the high water cut of the obtained products. According to the data for 2020, the average water cut in the main fields of Russia comprises at least 85%, with the mass ratio of produced oil and associated water approaching 1:7. The use of water-soluble polymers for waterproofing of horizontal wells can be considered a promising direction due to their efficiency in limiting water inflow in vertical and directional wells.
GEOLOGY
Background. Definition of local stratigraphical units, the main of which are formations, is important for geological mapping and correct understanding of the composition of sedimentary complexes. This task is yet to be solved for some territories. Thus, Upper Miocene deposits extend widely across the Rostov Dome in the southwest of Russia; however, the definition of formations there is still in its nascent phase.
Aim. Systematization of ideas about the local stratigraphical units of the Upper Miocene of the Rostov Dome, taking previous assumptions into account.
Materials and methods. An analysis of ideas related to the definition of formations in the Upper Miocene of the Rostov Dome was carried out. These ideas were systematized with a focus on the validity of the units based on the current stratigraphical code.
Results. An improved local stratigraphical scale of the Upper Miocene of the Rostov Dome is proposed. This scale implies defining the Taganrogskaya (Lower Sarmatian), Rostovskaya (Middle–Upper Sarmatian), Donskaya (lower Upper Maeotian), Merzhanovskaya (upper Upper Maeotian), and Aleksandrovskaya (Lower Pontian) formations. The correspondence of alternative units is shown: the Mokrochaltyrskaya and Berdanosovskaya formations correspond to the Rostovskaya Formation, while and the later proposed Rostovskaya Formation corresponds to the Donskaya and Merzhanovskaya formations. Discussion. The validity of the proposed local stratigraphical units is noted; the priority of defining the Taganrogskaya and Aleksandrovskaya formations is highlighted. The question of creating an automatic system for generalizing information about stratigraphical units is discussed.
Conclusion. The need in the parallel existence of alternative local stratigraphical scales of the Upper Miocene of the Rostov Dome is absent. However, subdividing the relevant deposits requires further discussion and refinement.
MINERALOGY, PETROGRAPHY, LITHOLOGY
Background. The minerogenic specialization of the Muzkol-Rangkul anticlinorium consists in industrial gemstone deposits of ruby, cordierite, almandine, aquamarine, topaz, tourmaline, scapolite, etc. Large ore objects in this area are unknown. Until recently, the area has had a negative assessment in terms of rare, rare earth, and noble metals.
Aim. To justify the identification of a previously unknown magnetic ring-type structure and to study the associated ore geochemical anomalies.
Materials and methods. Rock and mineral samples collected at the Chernogorskoye deposit in 2016 and 2018 were examined. The mineral composition were determined using a Polam-R211 petrographic microscope and confirmed by XRD analysis using a DRON-3M diffractometer (analyst A.V. Fedorov, Sergo Russian State University for Geological Prospecting). The chemical composition of mineral samples was studied by X-ray microanalysis using a Cameca SX 100 instrument (analyst N.N. Kononkova, Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry). The chemical compositions of rock samples was determined using an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer AXIOS Advanced (analyst T.G. Kuzminа, Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry).
Results. A ring-type intrusion composed of hornblende peridotites, hornblendites, and gabbroids was identified in the Muzkol-Rangkul anticlinorium, in the area of the Chernogorskoye gem scapolite deposit. The gabbroids here contact the metamorphic rocks of the Sarydzhilga formation along the ring fault. The geochemical anomalies of Co, Ni, W, Nb, Ti, and REE were revealed in the contour of the ring structure and along its periphery.
Conclusion. The ring-type intrusion identified by the authors is a source of geochemical anomalies.
GEOLOGICAL EXPLORATION TECHNIQUE
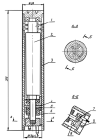
Background. Drilling vibrations may cause damage to the bit and early failure of downhole instruments. The main approach to solving this problem consists in measuring downhole vibrations while drilling by adding sensors near the bit in to the bottom hole assembly (BHA). When drilling vibrations are registered, measures are taken to avoid their reaching the critical values. If necessary the drilling stoops and the section is worked out to avoid accidents due to the high critical values. Not always drilling companies add such sensors to the BHA due to high price of the equipment. Constant problems with vibrations while drilling, require the creation of domestic low-cost autonomous equipment for measuring downhole vibrations and transmitting respective signals to the surface.
Aim. To develop domestic low-cost autonomous downhole vibration measuring equipment.
Materials and methods. Analysis of the experimental studies on drilling vibrations. Development technical solution such as domestic low-cost autonomous equipment for measuring downhole vibrations.
Results. The problem of drilling vibrations can be controlled by downhole measuring equipment located in the vicinity of the bit. The device under development is presented in the article.
Conclusion. In order to achieve maximum economic efficiency and avoid the costs of eliminating the consequences of vibrations, domestic low-cost autonomous downhole vibration measuring equipment should be developed to register torsional and longitudinal vibrations.
HISTORY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Background. The development of the oil and gas industry in the Caspian region is closely linked with the development of oil and gas resources of the Caspian Sea and adjacent territories. According to historical sources, it was in the Caspian region where the global offshore oil production was launched. Further, other countries used the experience gained in the Caspian region. Four main stages can be distinguished in the of the Caspian oil and gas complex, including the nascent (antique and medieval eras) stage; the initial stage of industrial development (from the 10th century to 1917); the Soviet stage of industrial development; and the modern stage of industrial development.
Aim. To study of the history of the development of the oil and gas industry in the Caspian region.
Materials and methods. The methods of retrospective, graphical, statistical, system-structural analysis were used in the work.
Results. Based on the results of the study, the main stages in the development of the oil and gas industry in the Caspian region were identified.
GEOLOGIC AND PROSPECTING EDUCATION ISSUES
Background. The dominant role of energy georesources in the mineral resources sector of Russian economy is considered. Achievements in this sector are determined by the quality of human capital. Successful implementation of the Strategy for the Development of the Mineral Resource Base of Russia until 2035 requires improved personnel training in the higher education system according to new educational programs in the disciplines of Applied Geology and Mining.
Aim. Assessment of the current state of the mining and geological industry in Russia, as well as its methodological and technological basis as an objective indicator of the economic and social development of the social system.
Materials and methods. Expert evaluation of the activities carried out by the Federal Subsoil Resources Management Agency in the direction of the geological study of energy resources.
Results. The conducted analysis of the sustainability of the mineral resources sector in the era of globalization and Russia’s historical experience of creating the uranium industry shows the need to further develop the nuclear energy sector. This process requires modifications in the engineering geological education to revive Russian traditions of training specialists in the field of uranium mining and treatment.
Conclusion. The prospects for increasing the mineral resources base of energy carriers and creating conditions for providing the country with energy raw materials should be supported by joint efforts of educational institutions and employers in the system of training geologists.
ISSN 2618-8708 (Online)